AG230
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein, porcine
Synonym(s):
GFAP
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Porcine
Quality Level
Assay
>99% (pure GFAP)
form
liquid
mol wt
calculated mol wt 49.44 kDa (428 a.a. spliced isoform; NP_001231326)
calculated mol wt 53.63 kDa (468 a.a. spliced isoform; XP_005668766)
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
concentration
1 mg/mL
technique(s)
ELISA: suitable
radioimmunoassay: suitable
western blot: suitable
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
Gene Information
pig ... GFAP(396562)
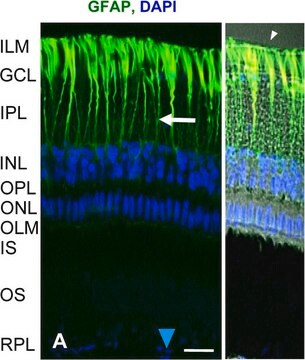
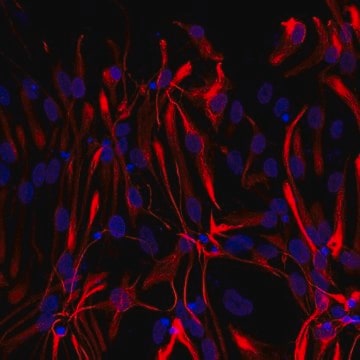
General description
Physical form
Storage and Stability
During shipment, small volumes of product will occasionally become entrapped in the seal of the product vial. For products with volumes of 200 μL or less, we recommend gently tapping the vial on a hard surface or briefly centrifuging the vial in a tabletop centrifuge to dislodge any liquid in the container′s cap.
Analysis Note
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service