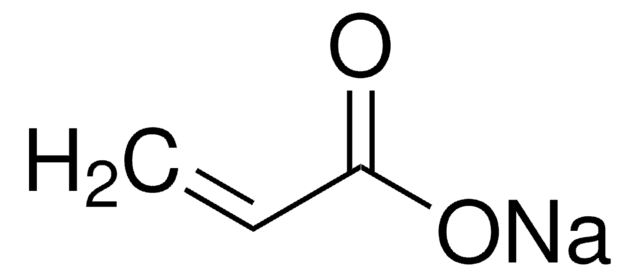
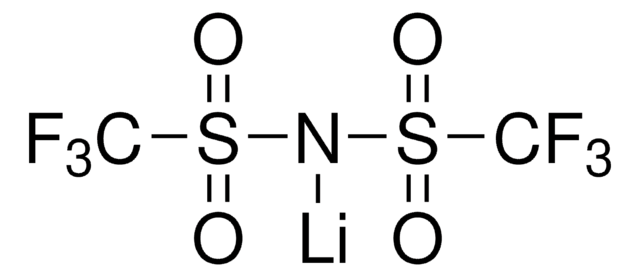
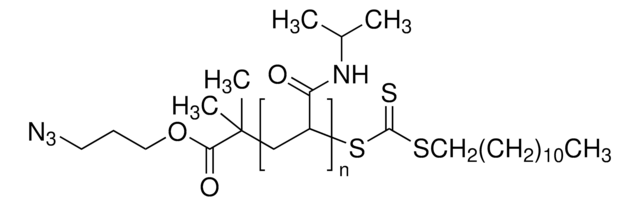
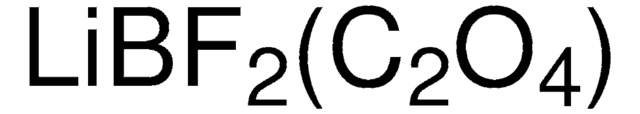773638
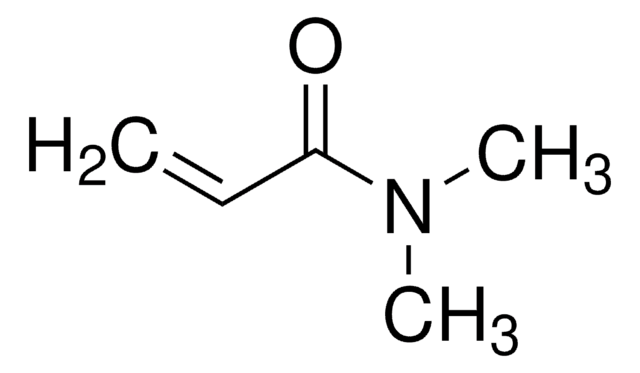
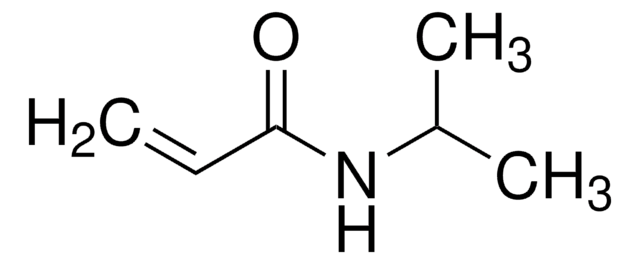
Poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide), DDMAT terminated
average Mn 10,000, PDI ≤1.1
Synonym(s):
PDMAM, polyDMAM, polydimethylacrylamide methylpropionic acid dodecyltrithiocarbonate
About This Item
Recommended Products
Related Categories
General description
Application
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization is rapidly moving to the forefront in construction of drug and gene delivery vehicles.
Over the past two decades, the rapid advance of controlled living polymerization (CLP) techniques.
Wide range of functional polymers for biomedical applications have been synthesized and structurally characterized. Several classes of polymers including biodegradable polymers, hydrophilic & amphiphilic polymers, and stimuli responsive polymers have been prepared using controlled and directed functionalization via "living" polymerization such as RAFT, ionic and ring opening polymerization. Selected polymers have been studied for their structure-properties relationship. "
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service