Selective Media for Bifidobacteria
Bifidobacteria in Dairy Manufacture
Media for the selective isolation, identification and enumeration of bifidobacteria like Bifidobacterium longum, infantis and brevi, are used for quality control in the manufacture of dairy products.
Bifidobacteria are Gram-positive, non-motile, rod-shaped and often branched anaerobic bacteria. They have a positive effect on the immune system and control intestinal pH. Bifidobacteria produce bacteriocins and bacteriocin-like inhibitory compounds which inhibit the growth of other bacteria.
B.longum is the best-characterised species in the genus Bifidobacterium. It is able to utilise a broad range of substrates for energy, such as plant polymers, glycoproteins and glyconjugates, as well as having specialised proteins for the catabolism of oligosaccharides.
Bifi dobacteria also have a unique hexose metaboliam called the bifid shunt. The key enzyme, fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase, is not found in any other gram-positive intestinal bacteria and therefore provides an ideal target for a diagnostic test.
In adult’s intestine, only 3–6 % of the faecal flora is composed of bifidobacteria while in breast-fed infants bifidobacteria can be up to 90 %. With increasing age the number of bifi dobacteria decrease. It was observed that babies and adults with lower numbers of bifi dobacteria have a higher risk for diarrhoea and allergies. For this reason bifi dobacterium are added as a probiotic supplement to infant formulas, drinks, yoghurts and a lot of other products.
Because of the wide use of bifi dus, we developed Bifidobacteria Selective Media (BSM), available as an agar or a broth, for standard for quality control. This allows for easy and fast quality control of yoghurt made with bifi dus and can be used to control the count of bifi dus bacteria.
Bifidobacteria grow very well on this medium whilst Lactobacillus and Streptococcus strains are inhibited. Bifidobacterium colonies grow within 24– 48 hours (occasionally up to three days because of the highly selective conditions). The Bifidobacterium colonies are purplebrown and therefore easy to differentiate from other organisms.
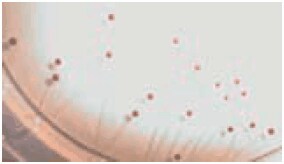
Figure 1.Yoghurt sample cultured on BSM Agar. Bifidobacteria appears as purplebrown colonies
In a Swiss governmental evaluation study for the enumeration of bifidobacteria in sour milk products, the traditional method was compared to Wilkins-Chalgren Agar with 100 mg/l mupirocine and BSM Agar. The traditional method gave significant differences while Wilkins-Chalgren Agar and BSM Agar showed similar results without any significant differences. The study remarked: “On the BSM Agar the bifidobacteria forms purple-brown colonies which made the enumeration easy”.
References
Um weiterzulesen, melden Sie sich bitte an oder erstellen ein Konto.
Sie haben kein Konto?