SML1648
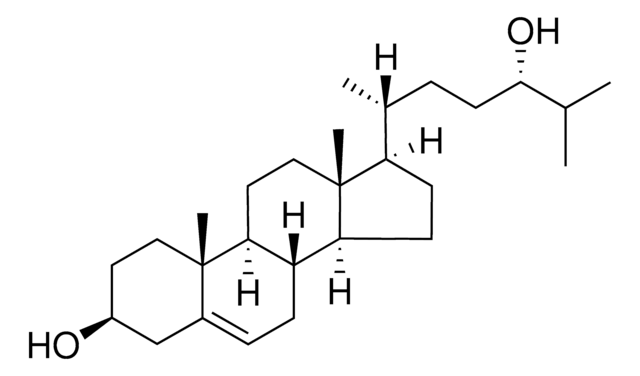
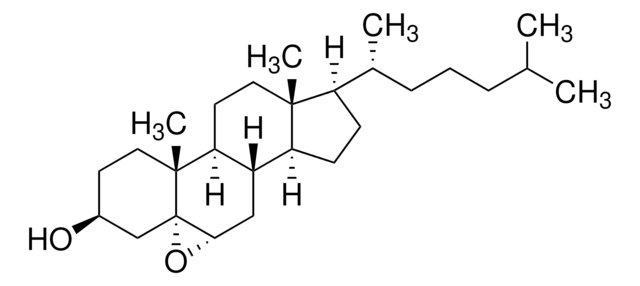
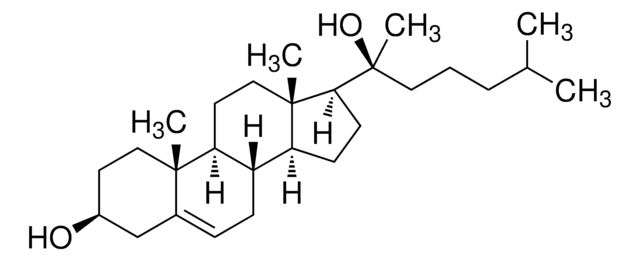
24(S)-Hydroxycholesterol
≥98% (HPLC)
Sinónimos:
24S-Hydroxycholesterol, 5-Cholesten-3β,24(S)-diol, Cerebrosterin, Cerebrosterol, Cholest-5-ene-3β,24-diol
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Quality Level
assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
powder
optical activity
[α]/D -45 to -52°, c = 1 in chloroform-d
storage condition
desiccated
color
white to beige
solubility
DMSO: 3 mg/mL, clear (warmed)
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C27H46O2/c1-17(2)25(29)11-6-18(3)22-9-10-23-21-8-7-19-16-20(28)12-14-26(19,4)24(21)13-15-27(22,23)5/h7,17-18,20-25,28-29H,6,8-16H2,1-5H3/t18-,20+,21+,22-,23+,24+,25+,26+,27-/m1/s1
InChI key
IOWMKBFJCNLRTC-XWXSNNQWSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Biochem/physiol Actions
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico