N8271
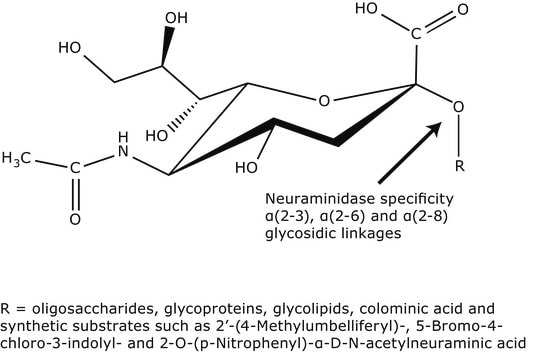
α(2→3,6,8,9) Neuraminidase from Arthrobacter ureafaciens
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, buffered aqueous solution
Sinónimos:
Neuraminidase from Arthrobacter ureafaciens, Acyl-neuraminyl Hydrolase, Sialidase
About This Item
Productos recomendados
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Quality Level
form
buffered aqueous solution
specific activity
≥135 units/mg protein
mol wt
88 kDa
95 kDa
foreign activity
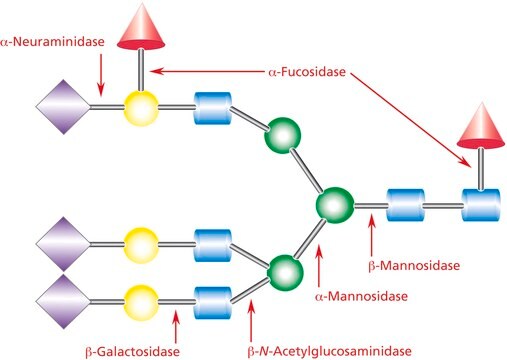
β-Galactosidase, α-mannosidase, β-hexosaminidase, α-fucosidase, and proteases, none detected
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Categorías relacionadas
Biochem/physiol Actions
Packaging
Unit Definition
Physical form
Preparation Note
Storage Class
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico