M1778
Mucina from porcine stomach
Type III, bound sialic acid 0.5-1.5 %, partially purified powder
Sinónimos:
MUC
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Productos recomendados
biological source
Porcine stomach
type
Type III
form
partially purified powder
composition
bound sialic acid, 0.5-1.5%
technique(s)
microbiological culture: suitable
solubility
NaOH: soluble 20 mg/mL
storage temp.
2-8°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
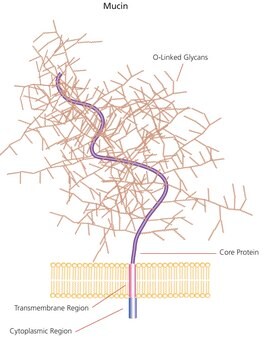
General description
Mucins or mucus glycoproteins are the main macromolecular components of mammalian mucus. It was also used in a study to evaluate the sputum smears concentrated by cyto-centrifugation for detection of acid-fast bacilli.
Application
Mucin from porcine stomach was used in studies on the binding site of the galactose-specific agglutinin PA-IL from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Mucus forms the protective cover for all epithelial surfaces. The major structural component of mucus is gel-forming mucins. The mucus layer covering the intestinal epithelium has the MUC2 mucin as its central molecule. MUC2 is produced by goblet cells.
Preparation Note
Prepared according to the method of Glenister, et al., for use in complex growth media for dental plaque bacteria.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Anastasia Matthies et al.
Applied and environmental microbiology, 74(15), 4847-4852 (2008-06-10)
The metabolism of isoflavones by gut bacteria plays a key role in the availability and bioactivation of these compounds in the intestine. Daidzein and genistein are the most common dietary soy isoflavones. While daidzein conversion yielding equol has been known
Helen Rose et al.
The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy, 63(3), 502-510 (2009-01-21)
The Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc) species are important opportunistic pathogens with intrinsic antibiotic resistance. They are also well known as contaminants of disinfectants, yet their biocide susceptibility has not been studied in detail. We investigated Bcc biocide susceptibility and correlated
Gabriel M F Almeida et al.
mBio, 10(6) (2019-11-21)
Metazoans were proposed to host bacteriophages on their mucosal surfaces in a symbiotic relationship, where phages provide an external immunity against bacterial infections and the metazoans provide phages a medium for interacting with bacteria. However, scarce empirical evidence and model
Leyuan Li et al.
Microbiome, 8(1), 33-33 (2020-03-13)
Human-targeted drugs may exert off-target effects or can be repurposed to modulate the gut microbiota. However, our understanding of such effects is limited due to a lack of rapid and scalable assay to comprehensively assess microbiome responses to drugs. Drugs
Jonathan E Phillips et al.
Journal of pharmacological and toxicological methods, 53(2), 160-167 (2006-03-02)
A method to measure the mucin concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid was developed to aid efforts to identify pharmacologically the mechanisms that modulate pathophysiological mucin secretion. Mucins are the major macromolecular components of mucus. In the airways, mucus is
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico