Documentos clave
C1184
Cellulase from Aspergillus niger
powder, ≥0.3 units/mg solid
Sinónimos:
1,4-(1,3:1,4)-β-D-Glucan 4-glucanohydrolase
Seleccione un Tamaño
Seleccione un Tamaño
About This Item
Productos recomendados
form
powder
Quality Level
specific activity
≥0.3 units/mg solid
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
greener alternative category
, Enabling
storage temp.
2-8°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
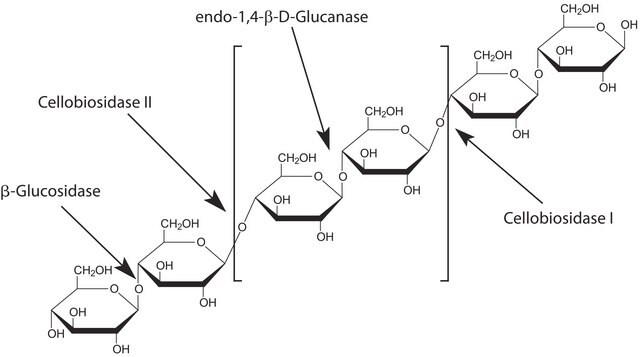
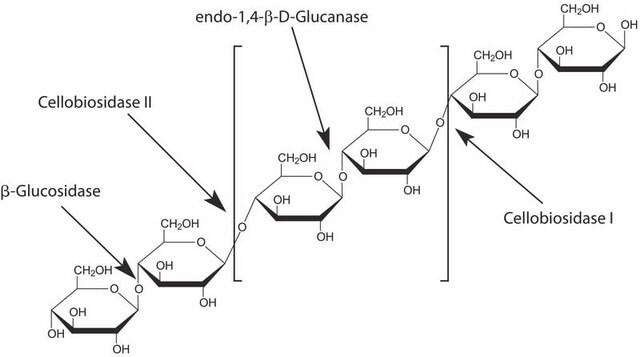
Cellulase belongs to the family of glycoside hydrolase,[1] which is secreted by various cellulolytic microorganisms.[2]
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Other Notes
substrate
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Necesita un COA de muestra?
Esto es un Certificado de análisis (COA) de muestra y es posible que no represente un lote de fabricación reciente para este producto específico.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico