K2755
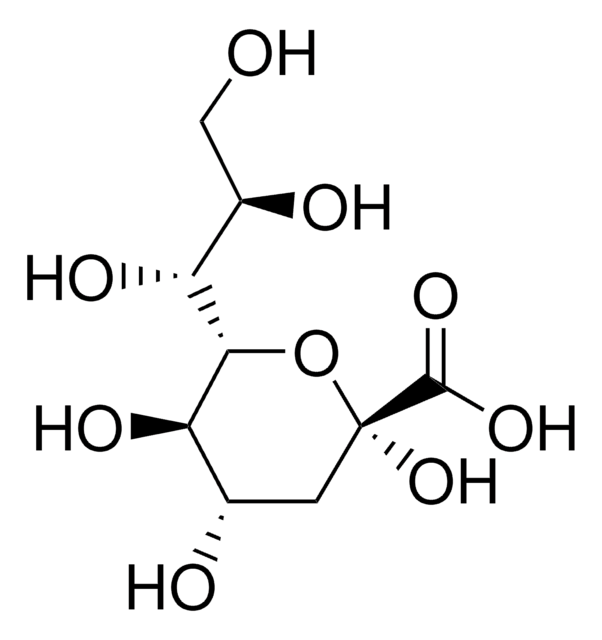
2-Keto-3-deoxyoctonate ammonium salt
≥97%
Sinónimos:
3-Deoxyoctulosonic acid, KDO
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula lineal:
C8H14O8 · NH3
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
255.22
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Productos recomendados
assay
≥97%
form
powder
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
N.OCC(O)C1OC(O)(CC(O)C1O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C8H14O8.H3N/c9-2-4(11)6-5(12)3(10)1-8(15,16-6)7(13)14;/h3-6,9-12,15H,1-2H2,(H,13,14);1H3
InChI key
UDJBBKGYARWWNJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Application
- Synthesis of KDO Analogues: A significant study focused on the synthesis of analogues of 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO), which includes compounds such as 2-Keto-3-deoxyoctonate ammonium salt. These analogues were evaluated as potential inhibitors of CMP-KDO synthetase, playing a critical role in the development of new therapeutic agents targeting bacterial infections and enhancing understanding of bacterial lipopolysaccharide synthesis (Luthman et al., 1987).
Biochem/physiol Actions
KDO is a sialic acid that is a component of bacterial lipopolysaccharides and a possible target for antibiotic development.
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Cadi Davies et al.
Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 9, 177-177 (2019-06-14)
Campylobacter jejuni outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) contain numerous virulence-associated proteins including the cytolethal distending toxin and three serine proteases. As C. jejuni lacks the classical virulence-associated secretion systems of other enteric pathogens that deliver effectors directly into target cells, OMVs
Karla Diaz-Ordaz et al.
BMC medical research methodology, 13, 127-127 (2013-10-24)
Previous reviews of cluster randomised trials have been critical of the quality of the trials reviewed, but none has explored determinants of the quality of these trials in a specific field over an extended period of time. Recent work suggests
Laura Cipolla et al.
Current drug discovery technologies, 6(1), 19-33 (2009-03-12)
Despite important advances made in the last century, infectious diseases caused by pathogenic microrganisms are still a major threat to human health. This is worsened by the occurrence of new forms of bacterial resistance against antibiotics, that are the main
Aloka B Bandara et al.
PloS one, 6(4), e19003-e19003 (2011-05-06)
Francisella tularensis is a category-A select agent and is responsible for tularemia in humans and animals. The surface components of F. tularensis that contribute to virulence are not well characterized. An electron-dense capsule has been postulated to be present around
Chiguang Feng et al.
PloS one, 7(4), e32359-e32359 (2012-04-13)
We previously reported that neuraminidase (NA) pretreatment of human PBMCs markedly increased their cytokine response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). To study the mechanisms by which this occurs, we transfected HEK293T cells with plasmids encoding TLR4, CD14, and MD2 (three components of
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico