724459
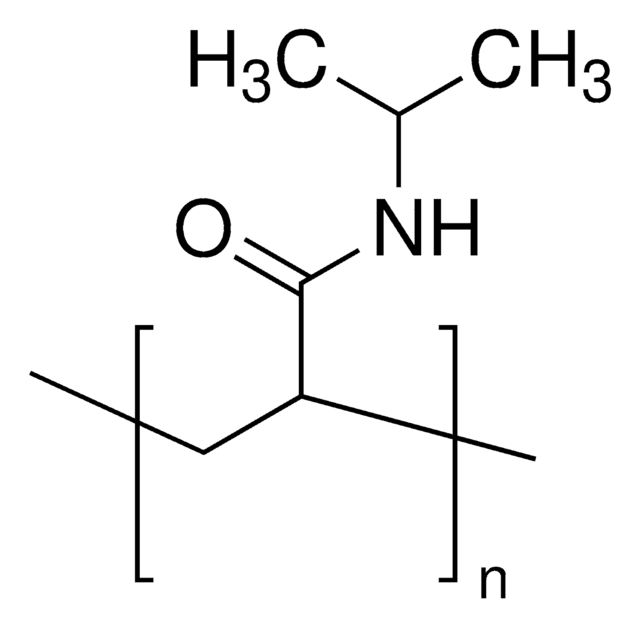
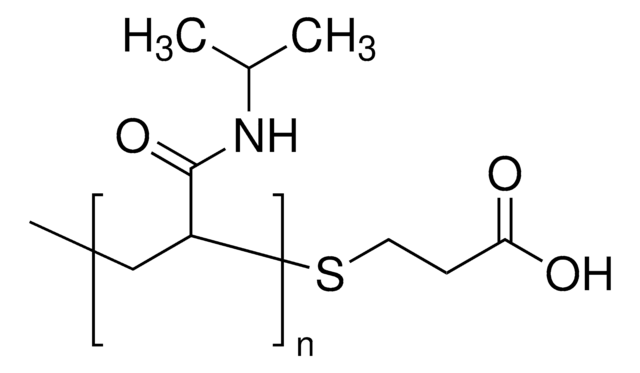
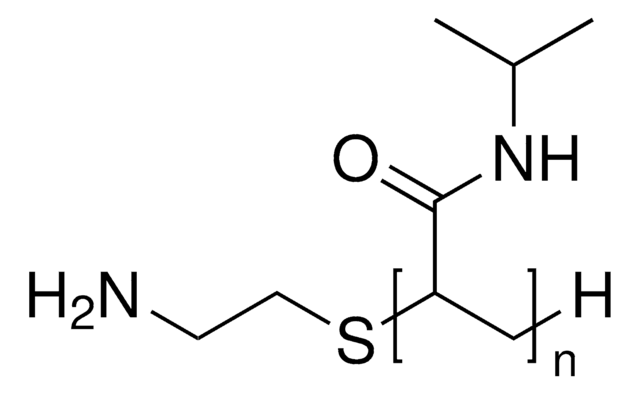
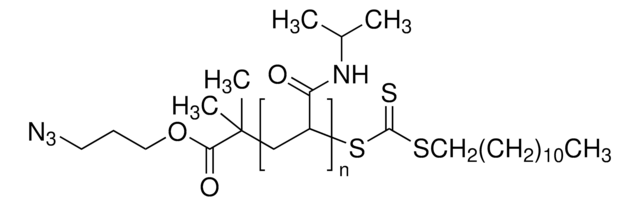
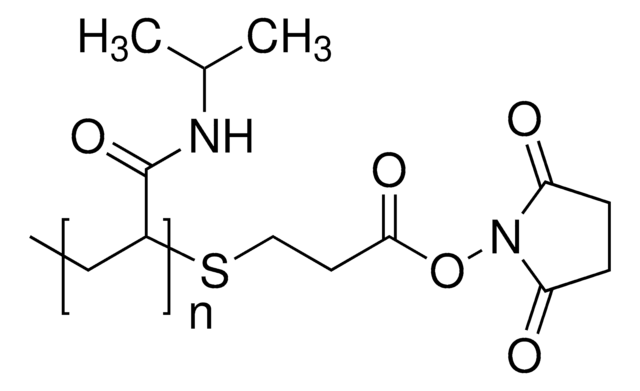
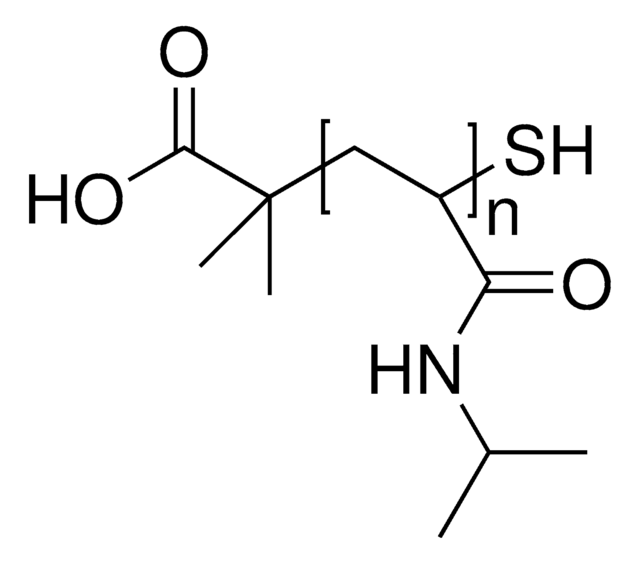
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), carboxylic acid terminated
average Mn 10,000
Sinónimos:
NIPAM polymer, PNIPAM-COOH, Polyacrylamide, functionalized polyNIPAM, functionalized polyacrylamide, polyNIPAM
About This Item
Productos recomendados
form
powder
mol wt
average Mn 10,000 by GPC (THF w/ 5%TEA, PS, RI)
average Mn 10,000
mp
>300 °C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Application
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 1
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Artículos
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), or PNIPAM, is a stimuli-responsive polymer that responds to changes in pH and temperature and has a LCST around 32 C.
Tissue engineering has become a key therapeutic tool in the treatment of damaged or diseased organs and tissues, such as blood vessels and urinary bladders.
By altering the physicochemical properties, smart or intelligent drug delivery systems can be designed to deliver therapeutic molecules on-demand. Learn more about the application of stimuli-responsive materials in drug delivery.
Wide range of functional polymers for biomedical applications have been synthesized and structurally characterized. Several classes of polymers including biodegradable polymers, hydrophilic & amphiphilic polymers, and stimuli responsive polymers have been prepared using controlled and directed functionalization via "living" polymerization such as RAFT, ionic and ring opening polymerization. Selected polymers have been studied for their structure-properties relationship. "
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico