637106
Iron(II,III) oxide
nanopowder, 50-100 nm particle size (SEM), 97% trace metals basis
Sinónimos:
Ferrosoferric oxide, Iron oxide black, Magnetite
About This Item
Productos recomendados
assay
97% trace metals basis
form
nanopowder
spherical
surface area
6-8 m2/g , estimated
particle size
50-100 nm (SEM)
mp
1538 °C (lit.)
density
4.8-5.1 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
bulk density
0.84 g/mL
application(s)
battery manufacturing
SMILES string
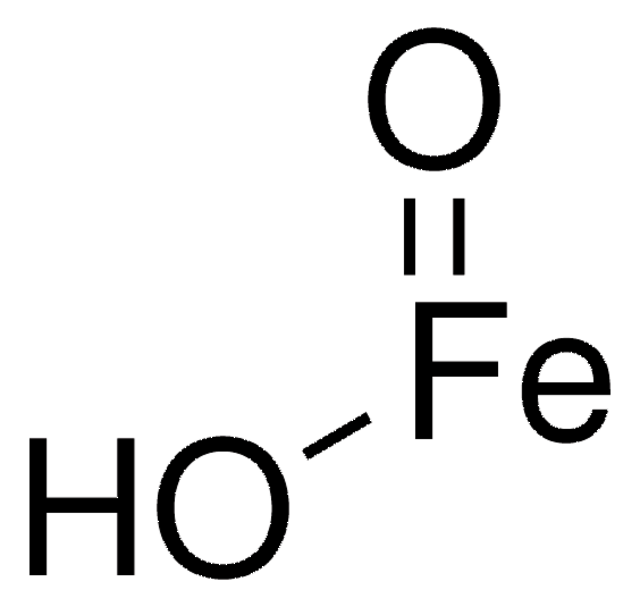
O=[Fe].O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O
InChI
1S/3Fe.4O
InChI key
SZVJSHCCFOBDDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Application
Analysis Note
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
nwg
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Professor Randal Lee (University of Houston, USA) discusses design considerations for iron oxide magnetic nanospheres and nanocubes used for biosensing, including synthetic procedures, size, and shape. The effects of these variables are discussed for various volumetric-based and surface-based detection schemes.
Currently, magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are attracting a lot of attention because of the possibility of many novel applications, especially in biomedical research.
An article concerning self-propagating reactions induced by mechanical alloying, presented by Sigma-Aldrich.com.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico