604852
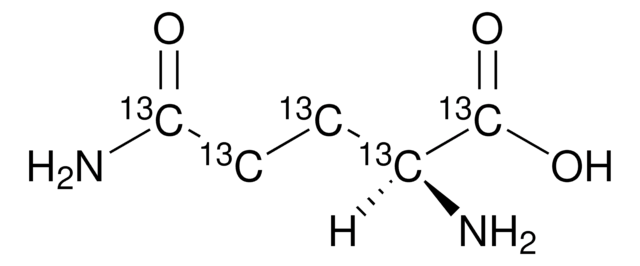
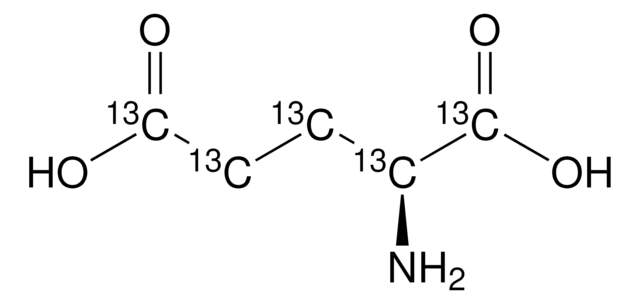
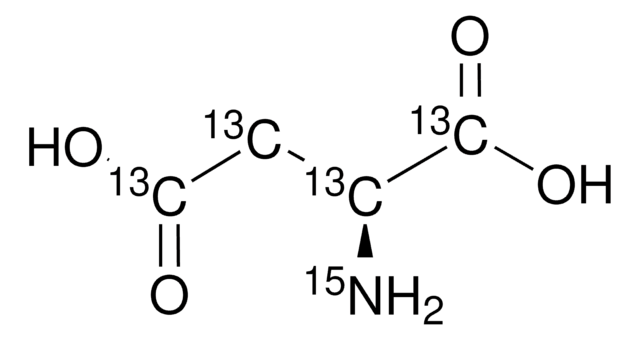
L-Aspartic acid-13C4
98 atom % 13C, 95% (CP)
Sinónimos:
(S)-(+)-Aminosuccinic acid-13C4, (S)-Aminobutanedioic acid-13C4, 13C Labeled L-aspartic acid
About This Item
Productos recomendados
isotopic purity
98 atom % 13C
Quality Level
assay
95% (CP)
form
solid
optical activity
[α]25/D +25.0°, c = 2 in 5 M HCl
mp
>300 °C (dec.) (lit.)
mass shift
M+4
SMILES string
N[13C@@H]([13CH2][13C](O)=O)[13C](O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H7NO4/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2H,1,5H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)/t2-/m0/s1/i1+1,2+1,3+1,4+1
InChI key
CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-UVYXLFMMSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Packaging
Storage Class
11 - Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico


![[2-(Methacryloyloxy)ethyl]dimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl)ammonium hydroxide 95%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/217/219/73c91e1c-0ee4-4b3d-bead-a6dc3d09d1da/640/73c91e1c-0ee4-4b3d-bead-a6dc3d09d1da.png)