292818
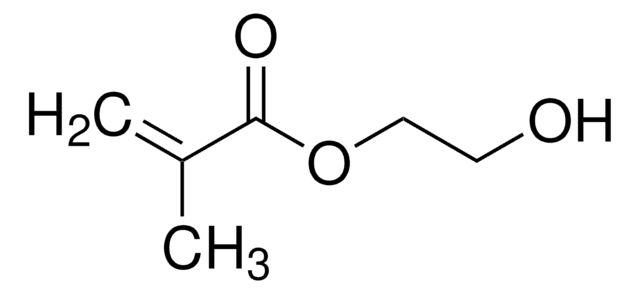
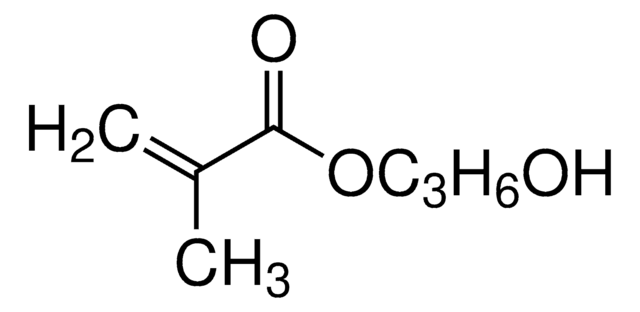
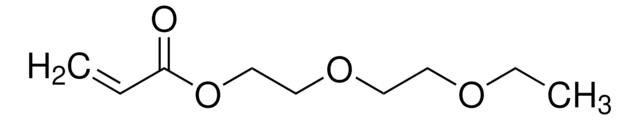
2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate
96%, contains 200-650 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Sinónimos:
Ethylene glycol monoacrylate
About This Item
Productos recomendados
vapor density
>1 (vs air)
Quality Level
vapor pressure
<0.1 mmHg ( 20 °C)
assay
96%
form
solid
contains
200-650 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
refractive index
n20/D 1.45 (lit.)
bp
90-92 °C/12 mmHg (lit.)
density
1.011 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
OCCOC(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C5H8O3/c1-2-5(7)8-4-3-6/h2,6H,1,3-4H2
InChI key
OMIGHNLMNHATMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
General description
Application
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
213.8 °F - closed cup
flash_point_c
101 °C - closed cup
ppe
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico