SAB4700447
Monoclonal Anti-MYC , (C-terminal) antibody produced in mouse
clone 9E10, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-Cellular myelocytomatosis oncogene, Anti-c-Myc
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.41
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
9E10, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
species reactivity
fusion proteins in all species, human
concentration
1 mg/mL
technique(s)
flow cytometry: suitable
isotype
IgG1
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... MYC(4609)
General description
The cellular myelocytomatosis (c-myc) gene mapped to human chromosome 8q24, is the cellular homologue of the v-myc gene originally isolated from an avian myelocytomatosis virus. c-myc is a member of MYC gene family. c-Myc gene codes for basic helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper (bHLH/LZ) transcription factor that regulates the G1-S cell cycle transition.
Immunogen
Synthetic peptide sequence (AEEQKLISEEDLL) corresponding to the C-terminal region of human c-Myc
Application
Monoclonal Anti-MYC, (C-terminal) antibody produced in mouse has been used in following studies:
- western blotting analysis
- chromatin immunoprecipitation quantitative PCR (ChIP-qPCR assays
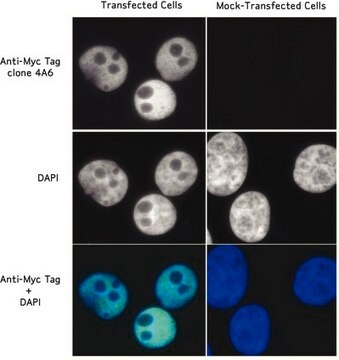
- immunofluorescence microscopy
The reagent is designed for Flow Cytometry analysis. Suggested working dilution is 1-5 μg/mL of sample. Indicated dilution is recommended starting point for use of this product. Working concentrations should be determined by the investigator. Membrane permeabilization is required.
Biochem/physiol Actions
The cellular myelocytomatosis (c-myc) oncogene plays a vital role in cellular proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and acts as transcriptional regulator of gene expression. c-Myc expression is essential and sufficient to assist most of the cells to enter DNA synthetic (S) phase of the cell cycle. The encoded protein plays a crucial role in vasculogenesis and angiogenesis during cancer development and progression. c-Myc interacts with its binding partner Max and activates the transcription of growth promoting genes such as cyclin D2, ornithine decarboxylase and E2F1 and it also represses the transcription of multiple genes, especially p21 and p27, by binding to the transcription initiator element (Inr) in a complex with Max and either Sp1 or Miz1. Overexpression of MYC in DLBCL (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma) results in poor outcome and invasive treatment when medicated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone (R-CHOP).
Features and Benefits
Evaluate our antibodies with complete peace of mind. If the antibody does not perform in your application, we will issue a full credit or replacement antibody. Learn more.
Physical form
Solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, with 15 mM sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
recommended
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Manling Xie et al.
Nature neuroscience, 25(1), 26-38 (2021-12-18)
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell 2 (TREM2) is linked to risk of neurodegenerative disease. However, the function of TREM2 in neurodegeneration is still not fully understood. Here, we investigated the role of microglial TREM2 in TAR DNA-binding protein 43
CSBF/C10orf99, a novel potential cytokine, inhibits colon cancer cell growth through inducing G1 arrest
Pan W
Scientific Reports (2014)
Positive feedback promotes mitotic exit via the APC/C-Cdh1-separase-Cdc14 axis in budding yeast
Hatano Y
Cellular Signalling, 28, 1545-1554 (2016)
Chen-Hui Li et al.
The Plant cell, 26(6), 2538-2553 (2014-06-08)
High salinity causes growth inhibition and shoot bleaching in plants that do not tolerate high salt (glycophytes), including most crops. The molecules affected directly by salt and linking the extracellular stimulus to intracellular responses remain largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate
Apoptotic signaling by c-MYC.
Hoffman B and Liebermann DA.
Oncogene, 27, 6462-6472 (2008)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service