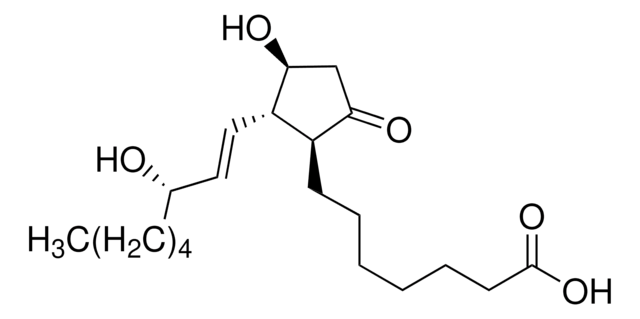
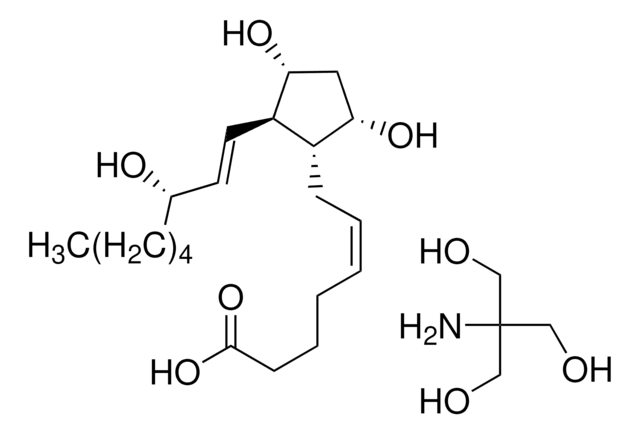
D8440
15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2
≥95% (HPLC), 1 mg/mL in methyl acetate
Synonym(s):
11-Oxoprosta-(5Z,9,12E,14E)-tetraen-1-oic acid, 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95% (HPLC)
form
liquid
concentration
1 mg/mL in methyl acetate
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
CCCCC\C=C\C=C1/[C@@H](C\C=C/CCCC(O)=O)C=CC1=O
InChI
1S/C20H28O3/c1-2-3-4-5-6-10-13-18-17(15-16-19(18)21)12-9-7-8-11-14-20(22)23/h6-7,9-10,13,15-17H,2-5,8,11-12,14H2,1H3,(H,22,23)/b9-7-,10-6+,18-13+/t17-/m0/s1
InChI key
VHRUMKCAEVRUBK-GODQJPCRSA-N
General description
Application
- to study its effect on lipid accumulation, viability/mitochondrial activity, and amount of vasculature in vascularized adipose tissue model
- as a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARγ) agonist to activate intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP)-PPARγ pathway
- as a supplement in culture medium for induced neural stem/progenitor cells (NSPCs) differentiation
Biochem/physiol Actions
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Central nervous system
Supplementary Hazards
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
15.8 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
-9 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service