CS0780
β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase Assay Kit
sufficient for 50 reactions (1 mL), sufficient for 500 reactions (100 μL)
Synonym(s):
Beta-NAG Activity Assay Kit
About This Item
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 50 reactions (1 mL)
sufficient for 500 reactions (100 μL)
Quality Level
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
human ... NAGLU(4669)
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Analysis Note
Kit Components Only
- Dilution Buffer 8 mL
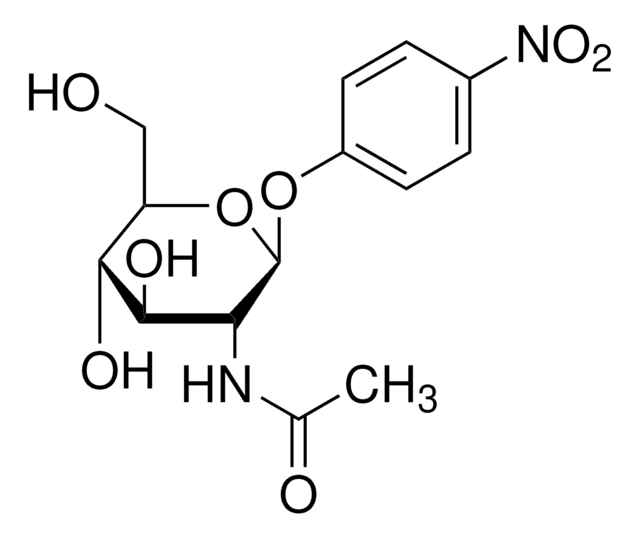
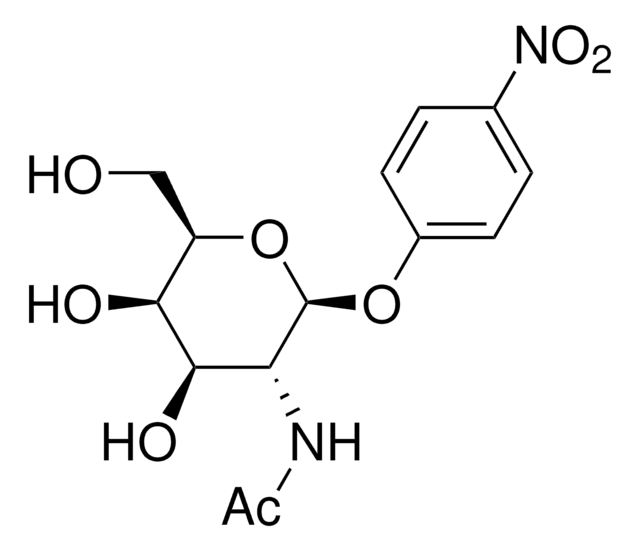
- 4-Nitrophenyl-N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide 50 mg
- Citrate Buffer Solution, 0.09 M 100 mL
- p-Nitrophenol Standard Solution, 10 mM 1 mL
- β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase from Jack beans 1 vial
- Sodium carbonate 5 g
related product
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 2 Oral
Target Organs
Liver,Kidney
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The isolation of subcellular fractions by centrifugation is a commonly used technique and is widely applicable across multiple cell and tissue types. Because organelles differ in their size, shape, and density, centrifugation can be easily employed to separate and purify organelle fractions from gently homogenized samples.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service