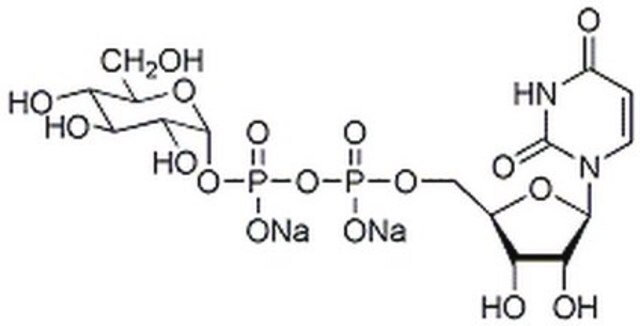
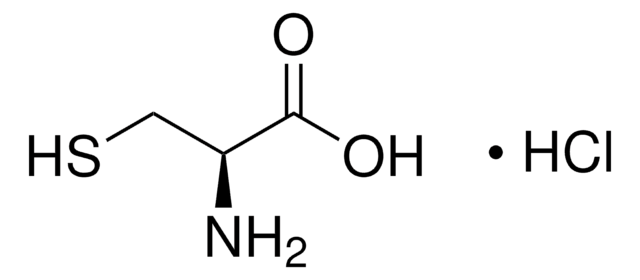
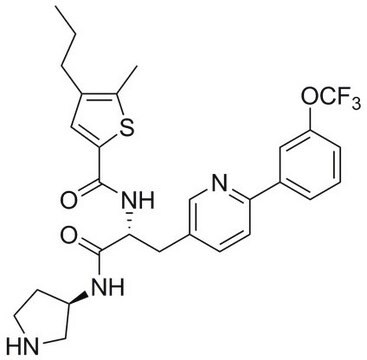
A1151
Anti-Albumin antibody produced in goat
fractionated antiserum, lyophilized
Synonym(s):
Albumin Detection Antibody, Anti-Albumin, Goat Anti-Albumin
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
goat
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in goat
antibody form
fractionated antiserum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
lyophilized
mol wt
antigen 65 kDa
species reactivity
human
packaging
vial of 2 mL lyophilized antiserum
technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunohistochemistry: suitable
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
human ... ALB(213)
Related Categories
General description
Albumin, the major protein produced by liver cells, represents more than half of the total protein content of human serum. Many other body fluids also contain albumin. Three major functions for serum albumin have been proposed: maintenance of osmotic pressure, transportation of a variety of substances and an endogenous source of amino acids. The primary sites of albumin degradation are not known, but the protein can be metabolized by almost every organ in the body. Determination of serum albumin levels is a widely used screening test in clinical medicine. A decrease in serum albumin levels may indicate disease states such as malnutrition, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, diabetes, gastrointestinal and hepatic diseases, thermal burns and pulmonary disease.
Goat polyclonal anti-Albumin antiserum is immunospecific for human albumin by immunoelectrophoresis against normal human serum and human albumin. Identity and purity of the specific antibody is established by immunoelectrophoresis (IEP). Electrophoresis of the antiserum followed by diffusion against anti-goat serum results in multiple arcs of precipitation, whereas against anti-goat IgG, it results in a single arc of precipitation in the γ region.
Immunogen
purified human albumin
Application
Goat polyclonal anti-Albumin antiserum is used to tag albumin for detection and quantitation by immunocytochemical and immunohistochemical (IHC) techniques. It is used as a probe to determine the presence and roles of albumin a variety of clinical indications.
Physical form
Lyophilized from 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Tetsu Akimoto et al.
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology, 284(6), C1625-C1632 (2003-02-28)
We have demonstrated that during culture under 5% O(2,) the addition of recombinant human VEGF or FGF2 to mouse embryonic aorta explants (thoracic level to lateral vessels supplying the mesonephros and metanephros) stimulates microvessel formation. Here we show that microvessel
G Grossmann et al.
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 82(6), 2003-2010 (1997-06-01)
Near-term newborn rabbits were exposed via the airways to a monoclonal antibody to surfactant protein B and ventilated for 0-120 min. Control animals received nonspecific rabbit or mouse immunoglobulin G, saline, or no material via the airways. Administration of the
Tetsu Akimoto et al.
Organogenesis, 2(1), 17-21 (2005-01-01)
Hypoxia exists widely in developing embryos where it may regulate blood vessel formation. VEGF and FGF2 produced in developing renal primordia (metanephroi) stimulate microvessel formation from embryonic thoracic aorta cultured under hypoxic conditions (HC) relative to room air (RA). The
Elliott L Rodriguez et al.
Journal of chromatography. A, 1638, 461683-461683 (2020-11-24)
Diabetes is characterized by elevated levels of blood glucose, which can result in the modification of serum proteins. The modification of a protein by glucose, or glycation, can also lead to the formation of advanced glycated end-products (AGEs). One protein
Mischa R Müller et al.
mAbs, 4(6), 673-685 (2013-05-17)
Advances in recombinant antibody technology and protein engineering have provided the opportunity to reduce antibodies to their smallest binding domain components and have concomitantly driven the requirement for devising strategies to increase serum half-life to optimise drug exposure, thereby increasing
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service