About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
for microscopy
Quality Level
form
liquid
shelf life
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
concentration
0.4%
technique(s)
microbe id | staining: suitable
color
blue to very dark blue
density
1.007 g/mL at 20 °C
εmax
1.4 at 603 nm in methanol
suitability
suitable for microscopy
application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
hematology
histology
storage temp.
room temp
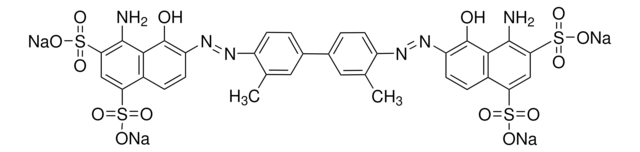
SMILES string
[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].Cc1cc(ccc1N=Nc2c(O)c3c(N)cc(cc3cc2S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)-c4ccc(N=Nc5c(O)c6c(N)cc(cc6cc5S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)c(C)c4
InChI
1S/C34H28N6O14S4.4Na/c1-15-7-17(3-5-25(15)37-39-31-27(57(49,50)51)11-19-9-21(55(43,44)45)13-23(35)29(19)33(31)41)18-4-6-26(16(2)8-18)38-40-32-28(58(52,53)54)12-20-10-22(56(46,47)48)14-24(36)30(20)34(32)42;;;;/h3-14,41-42H,35-36H2,1-2H3,(H,43,44,45)(H,46,47,48)(H,49,50,51)(H,52,53,54);;;;/q;4*+1/p-4
InChI key
GLNADSQYFUSGOU-UHFFFAOYSA-J
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- it is a routinely used for viability testing for diverse cell types including frozen sperm and aortic muscle cells exposed to antifungal agents.
- employed as a collagen stain in a Van Gieson procedure
- To stain amyloid, Trypan blue is considered as a blue alternative to Congo red in Puchtler-Bennhold stains.
- used as a fluorescent tracer of cell populations in embryology
- used as a tumor promoter modulating permeability of lysosomal membranes
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical form
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Carc. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service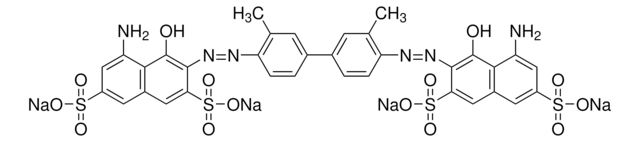



![Benzo[a]pyrene ≥96% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/253/820/be96d879-1811-46c0-8f11-612019691c2d/640/be96d879-1811-46c0-8f11-612019691c2d.png)