930792
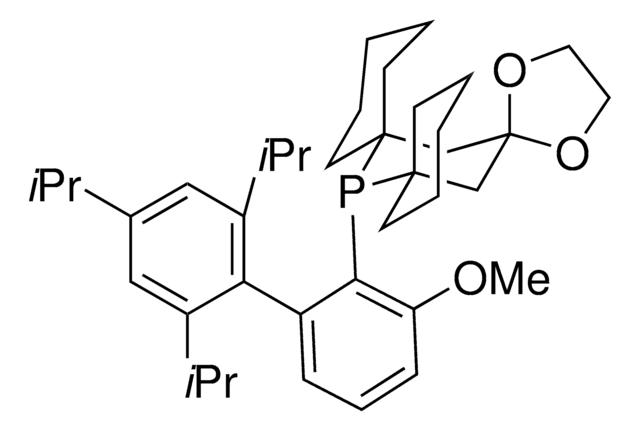
3-[1,3-Dihydro-4-(4-hydroxy-1-butyn-1-yl)-1-oxo-2H-isoindol-2-yl]-2,6-piperidinedione
≥95.0%
Synonym(s):
2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-[1,3-dihydro-4-(4-hydroxy-1-butyn-1-yl)-1-oxo-2H-isoindol-2-yl]
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥95.0%
form
powder
functional group
hydroxyl
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O=C1NC(=O)C(N2C(=O)C=3C=CC=C(C#CCCO)C3C2)CC1
InChI
1S/C17H16N2O4/c20-9-2-1-4-11-5-3-6-12-13(11)10-19(17(12)23)14-7-8-15(21)18-16(14)22/h3,5-6,14,20H,2,7-10H2,(H,18,21,22)
Related Categories
Application
Technology Spotlight: Degrader Building Blocks for Targeted Protein Degradation
Protein Degrader Building Blocks
Other Notes
Destruction of DNA-Binding Proteins by Programmable Oligonucleotide PROTAC (O′PROTAC): Effective Targeting of LEF1 and ERG
Small-Molecule PROTACS: New Approaches to Protein Degradation
Targeted Protein Degradation: from Chemical Biology to Drug Discovery
Impact of linker length on the activity of PROTACs
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Repr. 1B
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service
![3-[1,3-Dihydro-4-(5-hydroxy-1-pentyn-1-yl)-1-oxo-2H-isoindol-2-yl]-2,6-piperidinedione ≥95.0%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/165/184/ebc29f1b-f63f-4e48-afb5-b3aa4c69795a/640/ebc29f1b-f63f-4e48-afb5-b3aa4c69795a.png)