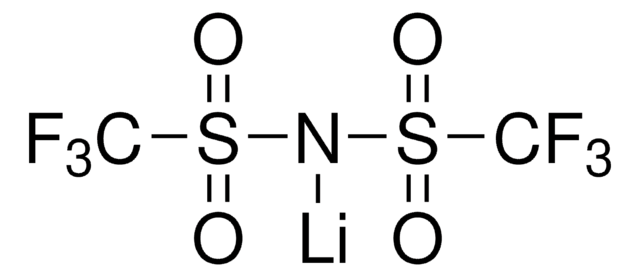
481548
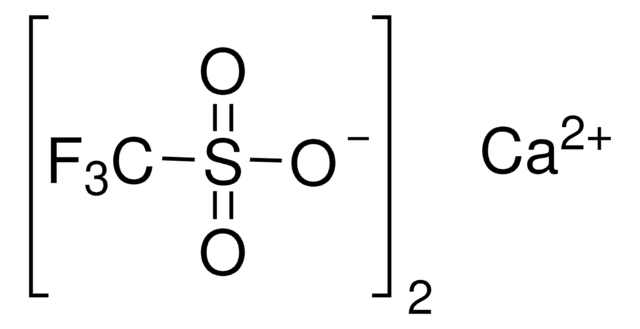
Lithium trifluoromethanesulfonate
99.995% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
LiTf, Lithium triflate, Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid lithium salt
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
for analytical purposes
Assay
99.995% trace metals basis
form
powder
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
impurities
≤60 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
mp
>300 °C (lit.)
application(s)
battery manufacturing
greener alternative category
SMILES string
[Li+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)C(F)(F)F
InChI
1S/CHF3O3S.Li/c2-1(3,4)8(5,6)7;/h(H,5,6,7);/q;+1/p-1
InChI key
MCVFFRWZNYZUIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- a polymeric layer for light-emitting electrochemical cells
- an electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries
- a recyclable catalyst for acetylation of alcohols and diacetylation of aldehydes
- a separator for supercapacitors
related product
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Dr. Sun reviews the recent advances in solid-state rechargeable batteries and cover the fundamentals of solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries, the theory of ion conduction, and the structures and electrochemical processes of solid-state Li batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely adopted as the most promising portable energy source in electronic devices because of their high working voltage, high energy density, and good cyclic performance.
Due to the adverse impact of the continued use of fossil fuels on the earth’s environment and climate, researchers have been asked to develop new approaches for producing power using renewable sources like wind and solar energy
Here, we present a short review of ionic liquid electrolytes used in state-of-the-art rechargeable batteries including high performance and low-cost aluminum batteries, non-flammable Li-based batteries, and high-cycling and stable dual-graphite batteries. We also outline the key issues explored so as to identify the future direction of IL development.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service