49055
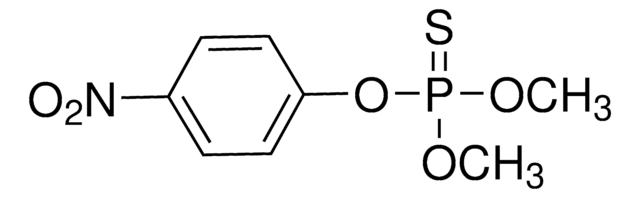
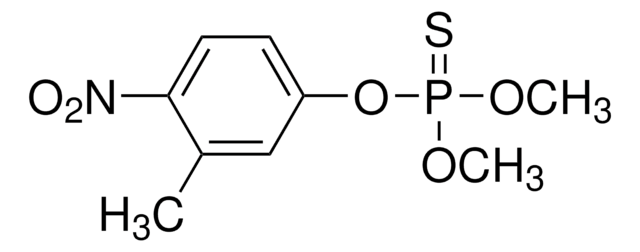
Parathion-methyl
PESTANAL®, analytical standard
Synonym(s):
O,O-Dimethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate, Methyl parathion
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C8H10NO5PS
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
263.21
Beilstein/REAXYS Number:
8905814
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12000000
PubChem Substance ID:
Recommended Products
grade
analytical standard
Quality Level
product line
PESTANAL®
CofA
current certificate can be downloaded
packaging
ampule of 500 mg
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
application(s)
agriculture
environmental
format
neat
storage temp.
room temp
SMILES string
COP(=S)(OC)Oc1ccc(cc1)[N+]([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C8H10NO5PS/c1-12-15(16,13-2)14-8-5-3-7(4-6-8)9(10)11/h3-6H,1-2H3
InChI key
RLBIQVVOMOPOHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Parathion-methyl is an organophosphate insecticide, which is extensively used for agricultural purposes. Its mode of action involves the inactivation of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in insects and also mammals. It undergoes degradation by soil microorganisms to yield p-nitrophenol as the product.
Application
Refer to the product′s Certificate of Analysis for more information on a suitable instrument technique. Contact Technical Service for further support.
Legal Information
PESTANAL is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Effect of paraoxon-methyl and parathion-methyl on DNA in human lymphocytes and protective action of vitamin C
Blasiak J and Kowalik J
Pest Management Science, 55(12), 1182-1186 (1999)
Isolation, characterization and identification of methyl parathion degrading bacteria from industrial waste
Vadukia, et al.
Journal of Cell and Tissue Research, 14(3), 4633-4633 (2014)
Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of daily oral doses of [14 C] methyl parathion in hens
Abu-Qare WA, et al.
Toxicology Letters, 125(1), 1-10 (2001)
Mohamed Abdel-Razek Saleh Abdel-Razek et al.
Journal of environmental science and health. Part. B, Pesticides, food contaminants, and agricultural wastes, 48(6), 449-461 (2013-03-05)
The goal of this study was to optimize methyl parathion (O,O-dimethyl-O-4-p-nitrophenyl phosphorothioate) degradation using a strain of Escherichia coli DH5α expressing the opd gene. Our results indicate that this strain had lower enzymatic activity compared to the Flavobacterium sp. ATCC
Scott A Trammell et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), 48(34), 4121-4123 (2012-03-22)
Using a low power green laser, we have demonstrated a rate acceleration of ~2-fold for the hydrolysis of methyl parathion by irradiating the plasmon absorption band of Au nanoparticles capped with a Cu(bpy) catalyst.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service