W3269
Monoclonal Anti-WDR62 antibody produced in mouse
~1.0 mg/mL, clone 3G8, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-C19orf14, Anti-WD repeat domain 62
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(2)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.41
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
3G8, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
antigen ~170 kDa
species reactivity
human
concentration
~1.0 mg/mL
General description
Monoclonal Anti-WDR62 (mouse IgG2a isotype) is derived from the hybridoma 3G8 produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from BALB/c mice immunized with a fusion protein encoding a fragment of human WDR62. WD repeat 62 is a member of WD-repeats and contains 15 WD repeats. WD-repeats consists of minimally conserved domains of 40-60 amino acids, which are initiated by glycine-histidine (GH) dipeptide 11 to 24 residues from the N-terminus and ends with tryptophan-aspartic acid (WD) dipeptide at the C terminus.
Application
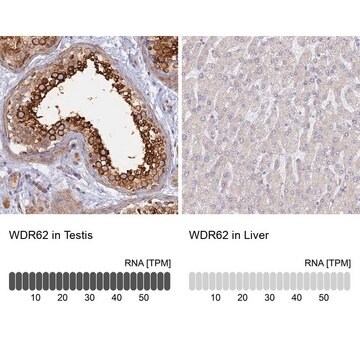
Monoclonal Anti-WDR62 antibody produced in mouse has been used in immunoblotting and immunofluorescence.
Biochem/physiol Actions
WD repeat 62 (WDR62) is identified in a phosphoproteome analysis as a protein associated with the mitotic spindle. It physically interacts with RNA-binding protein (RALY), TATA-binding protein (TBP), C1 or f103, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK9) and itself. WDR62 potentiates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity. Mutations in this gene are linked to microcephaly and cortical malformations.
Target description
WDR62 contains 15 WD repeats and has been identified in aphosphoproteome analysis as a protein associated with the mitotic spindle. WD40 proteins are implicated in many essential biologicalfunctions including adaptor/regulatory modules in signaltran
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Mutations in WDR62, encoding a centrosome-associated protein, cause microcephaly with simplified gyri and abnormal cortical architecture
Timothy WY, et al.
Nature Genetics, 42(11), 1015-1015 (2010)
Identification and analysis of a novel dimerization domain shared by various members of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) scaffold proteins
Cohen-Katsenelson K, et al.
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(10), 7294-7304 (2013)
Marie A Bogoyevitch et al.
Journal of cell science, 125(Pt 21), 5096-5109 (2012-08-18)
The impact of aberrant centrosomes and/or spindles on asymmetric cell division in embryonic development indicates the tight regulation of bipolar spindle formation and positioning that is required for mitotic progression and cell fate determination. WD40-repeat protein 62 (WDR62) was recently
D Li et al.
Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 58(14), 2085-2097 (2002-01-30)
Defined by the presence of four or more repeating units containing a conserved core of approximately 40 amino acids that usually ending with tryptophan-aspartic acid (WD), WD-repeat proteins belong to a large and fast-expanding conservative protein family. As demonstrated by
Ksenya Cohen-Katsenelson et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 288(10), 7294-7304 (2013-01-24)
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) form a kinase tier module in which MAPK, MAP2K, and MAP3K are held by scaffold proteins. The scaffold proteins serve as a protein platform for selective and spatial kinase activation. The precise mechanism by which the
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service