M3770
Micrococcus lysodeikticus ATCC No. 4698
suitable for substrate for the assay of lysozyme, lyophilized cells
Synonym(s):
Micrococcus luetus
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(4)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
form
lyophilized cells
Quality Level
suitability
suitable for substrate for the assay of lysozyme
storage temp.
−20°C
Application
Micrococcus lysodeikticus ATCC No. 4698 has been used in a study to assess lysozyme separation by hollow-fibre ultrafiltration. It has also been used in a study to investigate the encapsulation of protein drugs in biodegradable microparticles.
Lysozyme lysates harvested from cultures of Micrococcus lysodeikticus were attached to sepharose and used for affinity chromatography to isolate various bacteriolytic enzymes.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Micrococcus luetus is a Gram-positive bacteria that is identified by the release of yellow water-insoluble pigments. This species requires succinic acid for its growth and is found to be susceptible to β-lytic metalloendopeptidase lyses by Lysobacter enzymogenes. Its membrane includes enzymes that participate in the prenylation reactions by utilizing prenyl pyrophosphates as donors. M. luteus is known to be used for cloning the cis-prenyl transferase gene.
Quality
Contains polynucleotide phosphorylase.
Unit Definition
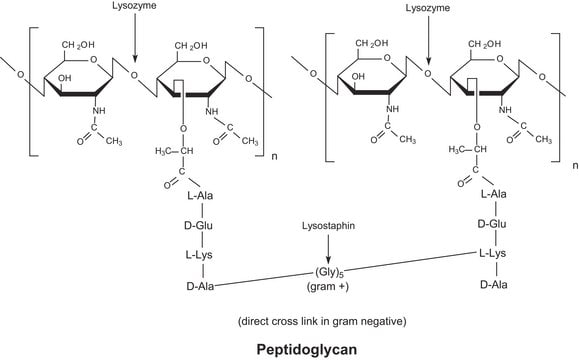
One unit will lyse 0.6 μg of Micrococcus lysodeikticus per minute by turbidimetric detection at 600 nm when suspended in buffer at pH 6.2 at 25 °C.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Tania Jauslin et al.
mBio, 12(1) (2021-02-18)
Ingestion and killing of bacteria by phagocytic cells protect the human body against infections. While many mechanisms have been proposed to account for bacterial killing in phagosomes, their relative importance, redundancy, and specificity remain unclear. In this study, we used
Tracking molecular recognition at the atomic level with a new protein scaffold based on the OB-fold.
John D Steemson et al.
PloS one, 9(1), e86050-e86050 (2014-01-28)
The OB-fold is a small, versatile single-domain protein binding module that occurs in all forms of life, where it binds protein, carbohydrate, nucleic acid and small-molecule ligands. We have exploited this natural plasticity to engineer a new class of non-immunoglobulin
J C Cox et al.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, 9(10), 2525-2531 (2001-09-15)
The in vitro selection of nucleic acid binding species (aptamers) is frequently repetitive, time-consuming, and poorly adapted to high-throughput applications. We have adapted automated workstations to select anti-protein aptamers; as an example, we demonstrated the selection of anti-lysozyme aptamers that
Marion Le Coadic et al.
PloS one, 8(1), e53259-e53259 (2013-01-10)
Dictyostelium discoideum has largely been used to study phagocytosis and intracellular killing of bacteria. Previous studies have shown that Phg1A, Kil1 and Kil2 proteins are necessary for efficient intracellular killing of Klebsiella bacteria. Here we show that in phg1a KO
Edward J Taylor et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 20(22) (2019-11-09)
Muramidases/lysozymes are important bio-molecules, which cleave the glycan backbone in the peptidoglycan polymer found in bacterial cell walls. The glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 22 C-type lysozyme, from the folivorous bird Opisthocomus hoazin (stinkbird), was expressed in Aspergillus oryzae, and a
Protocols
Enzymatic Assay of Achromopeptidase
This enzymatic rate determination may be used for Lysozyme products. It is not to be used to assay recombinant or insoluble Lysozyme on agarose.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service