565785
β-Secretase Activity Assay Kit, Fluorogenic
Synonym(s):
BACE Activity Assay Kit, Fluorogenic
About This Item
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 100 tests
Quality Level
manufacturer/tradename
Calbiochem®
storage condition
OK to freeze
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
protect from light
input
sample type tissue extract(s)
sample type purified enzyme(s) (BACE)
sample type cell lysate
detection method
fluorometric
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Components
Warning
Principle
Preparation Note
Storage and Stability
Other Notes
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Muta. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service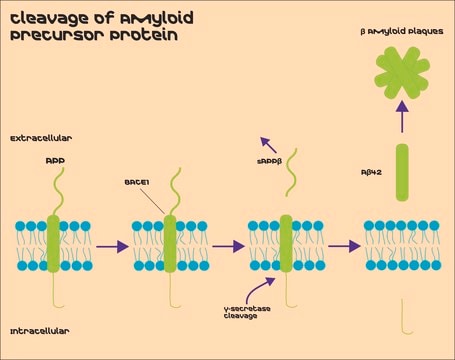


![MCA-[Asn670, Leu671]-Amyloid β/A4 Precursor Protein 770 Fragment 667-676-DNP-Lys-Arg-Arg-NH2 ≥90% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/images/375/511/f63f11a7-86de-45c4-95a0-7afa616bb265/640/f63f11a7-86de-45c4-95a0-7afa616bb265.jpg)