Purification of Protein A-Tagged Proteins
Recombinant tagged proteins containing a protein A tag can be purified on IgG Sepharose® 6 Fast Flow. The AC medium is based on the Sepharose® 6 Fast Flow matrix, with human IgG covalently coupled to it. The mechanical characteristics of this Fast Flow medium allows high flow velocities (up to 400 cm/h) to be used for rapid and convenient single-step purification of protein A-tagged protein conjugates produced in prokaryotic expression systems. Up to 2 mg/ml protein A can be bound to the ligand at pH 7.5.
IgG Sepharose® 6 Fast Flow is also suitable for tandem affinity purification (TAP) of protein complexes.
An alternative eluent is 0.1 M glycine-HCl, pH 3.0. Chaotropic agents may also be used for elution.
Characteristics of IgG Sepharose® 4 Fast Flow are shown in Table 1.
| Ligand | Composition | pH stability* | Particle size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human polyclonal IgG | IgG coupled to Sepharose® Fast Flow by the cyanogen bromide method. | Short term 3–10 Long term 3–10 | 90 µm |
* Short term refers to the pH interval for regeneration, cleaning-in-place and sanitization procedures. Long term refers to the pH interval over which the medium is stable over a long period of time without adverse effects on its subsequent chromatographic performance.
Performing a separation using IgG Sepharose® 6 Fast Flow
| Binding buffer: Wash buffer: Elution buffer: Neutralization buffer: | 0.05 M Tris-HCl, 0.15 M NaCl, 0.05% Tween 20, pH 7.6 5 mM ammonium acetate, pH 5.0 0.5 M acetic acid, adjusted to pH 3.4 with ammonium acetate 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 9.0 |
Purification
- Pack the column (Characteristics of Dextrin Sepharose High Performance products) and wash with at least 5 column volumes of binding buffer.
- Equilibrate the column with approximately 5 column volumes of binding buffer.
- Wash with 2–3 column volumes of acetic acid followed by 5 column volumes of binding buffer.
- Apply the sample.
- Wash with 10 column volumes binding buffer.
- Wash with 2 column volumes of wash buffer or until no material appears in the eluent (determined by UV absorbance at A280 nm).
- Elute with 2–5 column volumes of elution buffer.*
- Immediately re-equilibrate the column with binding buffer until the eluent reaches pH 7.0 (the IgG may denature if left at a lower pH).
* Since elution conditions are quite harsh, it is recommended to collect fractions into neutralization buffer (60 µL – 200 µL 1 M Tris-HCl, pH 9.0 per ml fraction), so that the final pH of the fractions will be approximately neutral.
This method, while giving a concentrated eluate, can only be used if the fusion product is stable under the acid conditions.
Application example
| Column: | IgG Sepharose® 6 Fast Flow (0.5 × 2.5 cm) |
|---|---|
| Sample: | Bacterial suspension containing ZZ-IGF-1 fusion protein, automatically sampled from fermentation broth, 500 µl |
| Binding buffer: | 0.05 M Tris-HCl, 0.05% Tween 20, pH 7.6 |
| Wash buffer: | 10 mM ammonium acetate, pH 4.6 |
| Elution buffer: | 0.2 M acetic acid, pH 3.2 |
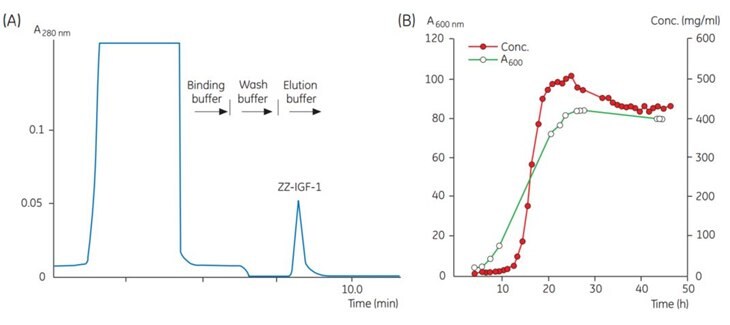
Figure 1.Chromatogram of a sample taken at one time point during fermentation. (B) Results from automatic monitoring of the product concentration during fermentation. Concentration of ZZ-IGF-1 is determined by integration of the ZZ-IGF-1 peak obtained during each chromatographic analysis. Bacterial density is measured manually at A600 nm.
Chemical stability
Avoid reducing agents such as 2-mercaptoethanol or DTT since they may disrupt disulfide bonds within the IgG ligand.
Storage
Wash with 5 column volumes of 20% ethanol at neutral pH and store at +4 °C to +8 °C.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?