Cleavage and Purification of GST-Tagged Protein Bound to GSTrap
Recommended buffers
Purification and Cleavage
The protocol below is an example optimized for 8 mg of target protein. It is worth estimating how much target protein is applied to the column, as this allows one to minimize the amount of protease added.
- Fill the syringe or pump tubing with distilled water. Remove the stopper and connect the column to the syringe (use the connector supplied), laboratory pump, or chromatography system “drop to drop” to avoid introducing air into the system.
- Remove the snap-off end at the column outlet.
- Wash out the ethanol with 3 to 5 column volumes of distilled water.
- Equilibrate the column with at least 5 column volumes of binding buffer. Recommended flow rates are 1 mL/min (1 mL column) and 5 mL/min (5 mL column).
- Apply the pretreated sample using a syringe fitted to the Luer connector or by pumping it onto the column. For best results, use a flow rate of 0.2 to 1 mL/min (1 mL column) and 0.5 to 5 mL/min (5 mL column) during sample application.
- Wash with binding buffer (generally at least 5 to 10 column volumes) until the absorbance reaches a steady baseline or no material remains in the effluent. Maintain a flow rate of 1 to 2 mL/min (1 mL column) and 5 to 10 mL/min (5 mL column) for washing.
- (a) For PreScission Protease and Factor Xa, wash the column with 10 column volumes of cleavage buffer.
(b) For thrombin, proceed to step 8b.
(c) For Factor Xa, proceed to step 8c.
- (a) Prepare the PreScission Protease mix:
-For GSTrap FF 1 mL columns, mix 80 µL (160 units) of PreScission Protease with 920 µL of PreScission cleavage buffer at 5 °C.
-For GSTrap FF 5 mL columns, mix 400 µL (800 units) of PreScission Protease with 4.6 mL of PreScission cleavage buffer at 5 °C.
(b) Prepare the thrombin mix:
- For GSTrap FF 1 mL columns, mix 80 µL (80 units) of thrombin solution with 920 µL of PBS.
- For GSTrap FF 5 mL columns, mix 400 µL (400 units) of thrombin solution with 4.6 mL of PBS.
(c) Prepare the Factor Xa mix:
-For GSTrap FF 1 mL columns, mix 80 µL (80 units) of Factor Xa solution with 920 µL of Factor Xa cleavage buffer.
-For GSTrap FF 5 mL columns, mix 400 µL (400 units) of Factor Xa solution with 4.6 mL of Factor Xa cleavage buffer.
- Load the protease mix onto the column using a syringe and the connector supplied. Seal the column with the top cap and the stopper supplied.
- (a) For PreScission Protease, incubate the column at 5 °C for 4 h.
(b) For thrombin and Factor Xa, incubate the column at room temperature (22 °C to 25 °C) for 2 to 16 h.
The incubation times are starting points and may need to be changed for an optimal yield of cleaved target protein.
- Fill a syringe with 3 mL (1 mL column) or 15 mL (5 mL column) of cleavage buffer. Remove the top cap and stopper from the column and attach the syringe. Avoid introducing air into the column.
- Begin elution of the cleaved target protein. Maintain flow rates of 1 to 2 mL/min (1 mL column) or 5 to 10 mL/min (5 mL column), and collect the eluate (0.5 to 1 mL/tube for 1 mL column, 1 to 2 mL/tube for 5 mL column).
For PreScission Protease: The eluate will contain the protein of interest, while the GST moiety of the tagged protein and the PreScission Protease (also GST-tagged) will remain bound to the Glutathione Sepharose column. This means that the protein of interest will not be contaminated with protease and thus no additional purification will be required to purify the target protein from the protease.
For thrombin and Factor Xa: The eluate will contain the protein of interest and thrombin or Factor Xa, respectively, while the GST moiety of the tagged protein will remain bound to the Glutathione Sepharose column. Thrombin or Factor Xa can be removed from the protein of interest in one step using a HiTrap Benzamidine FF (high sub) column in series after the GSTrap column. In this process, the cleaved, tagged protein and thrombin or Factor Xa is washed from the GSTrap column onto the HiTrap Benzamidine FF (high sub) column. This second column captures the thrombin or Factor Xa, thus enabling the collection of free protein in the eluent. Refer to the application on page 87 for an example of the purification and on-column cleavage of GST-tagged SH2 domain using thrombin and GSTrap FF, with sample cleanup accomplished using HiTrap Benzamidine FF (high sub) column in series with GSTrap FF.
Application Examples
1. Purification of human hippocalcin using GSTrap FF columns in series with on-column cleavage by PreScission Protease
The gene for human hippocalcin, a member of the neuron-specific calcium-binding protein family, was cloned into a pGEX vector containing a PreScission Protease site adjacent to the GST tag. The expressed tagged protein was captured on a GSTrap FF 1 mL column. The column was then incubated overnight at 4 °C and for an additional 2 h at room temperature with PreScission Protease (which is GST-tagged itself). Following on-column cleavage, a second GSTrap FF 1 mL column was placed in series after the first to remove any PreScission Protease, uncleaved GST-tagged protein, or free GST tag that could co-elute with the sample during the additional wash with binding buffer (Figure 5.3). For every gram of wet E. coli cells, 10 mg of pure, untagged hippocalcin was obtained.
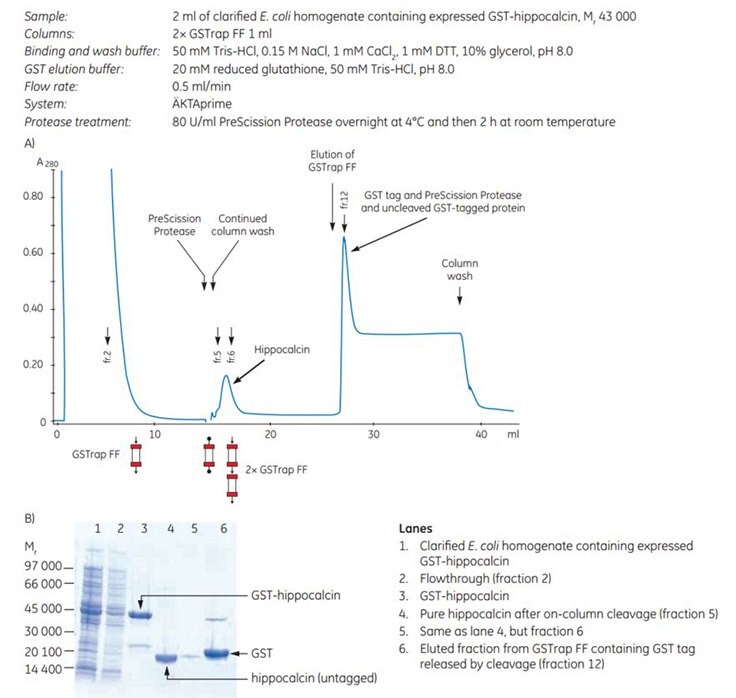
Figure 5.3. Purification of human hippocalcin-GST-tagged protein with on-column cleavage and post-cleavage removal of PreScission Protease using GSTrap FF columns. A) Chromatogram showing purification of hippocalcin. B) SDS-PAGE analysis of various sample processing steps. ExcelGel SDS Gradient, 8–18%, Coomassie blue staining.
2. Automatic removal of the GST tag with PreScission Protease
This example of automated tag removal uses ÄKTAxpress. All multistep purification protocols in ÄKTAxpress can be combined with automated on-column tag cleavage. Tag cleavage is always performed on the affinity column prior to further purification steps. When the cleaved protein has been eluted, the affinity column is regenerated and affinity tag, tagged protease, and remaining uncleaved protein are collected in a separate outlet. The procedure involves binding the tagged protein, injection of protease, incubation, elution of cleaved protein, and collection in capillary loop(s), followed by further purification steps.
The example, Figure 5.4 shows purification results for a GST-tagged protein, GST-purα (Mr 61 600), expressed in E. coli. The Mr of the cleaved product is 35 200. After harvest, cell lysis was performed by sonication. The samples were clarified by centrifugation prior to sample loading. Affinity chromatography and gel filtration were performed on ÄKTAxpress using columns as indicated in the figure. The purity of each sample was analyzed by SDS-PAGE (Coomassie staining). The reduced samples were applied on an ExcelGel SDS-polyacrylamide gel.
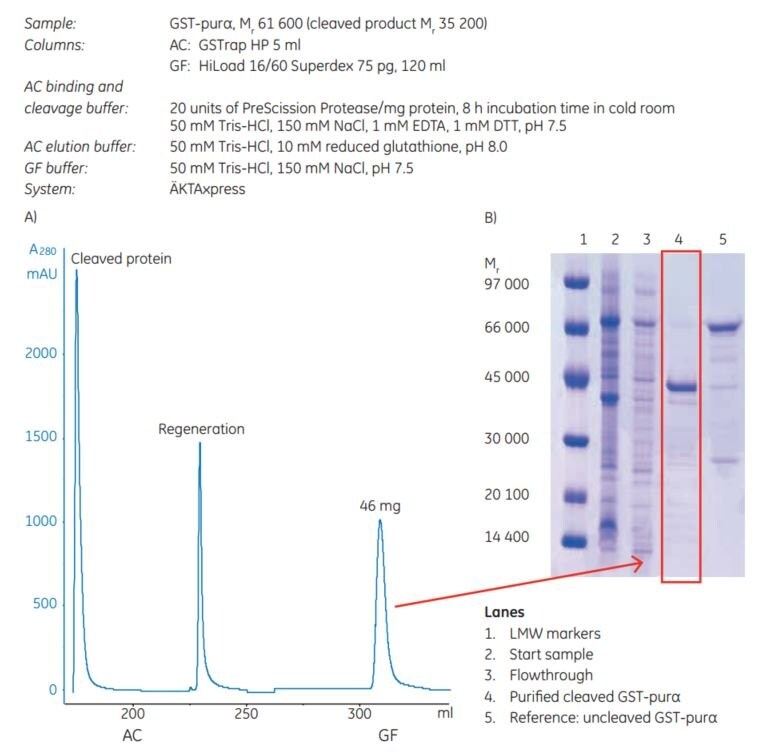
Figure 5.4. (A) Two-step protocol for automatic GST-tagged protein cleavage with PreScission Protease and purification. AC = affinity chromatography. GF = gel filtration. (B) Analysis by SDS-polyacrylamide gel (Coomassie staining) of the untagged target protein after purification and cleavage.
3. On-column cleavage of a GST-tagged protein using thrombin on a GSTrap FF column
To demonstrate the efficiency of on-column cleavage in conjunction with purification, a GST-tagged protein containing the recognition sequence for thrombin, was applied to GSTrap FF 1 mL. After washing, the column was filled by syringe with 1 mL of thrombin solution (20 U/mL in PBS, pH 7.3) and sealed using the supplied connectors. After incubation for 16 h at room temperature, the target protein minus the GST moiety was eluted using PBS, pH 7.3, and the bound GST was subsequently eluted using elution buffer (Figure 5.5). The cleavage reaction yield was 100%. Intact GST-tagged protein was not detected in the eluate by SDS-PAGE and silver staining (Figure 5.5C, lane 5).
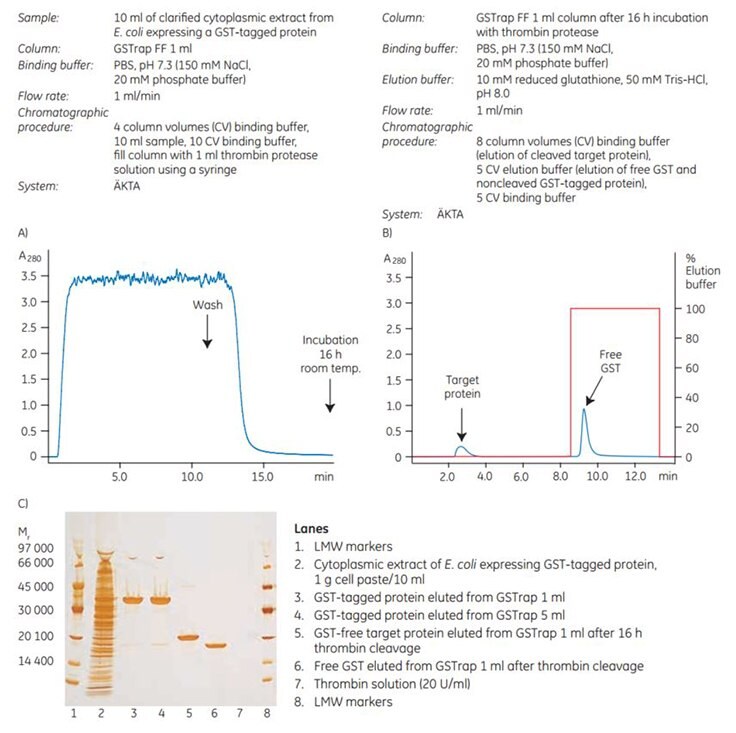
Figure 5.5. On-column thrombin cleavage of a GST-tagged protein. (A) Equilibration, sample application, and washing of a GST-tagged protein on GSTrap FF 1 mL were performed using ÄKTA chromatography system. After washing, the column was filled by syringe with 1 mL of thrombin (20 U/mL) and incubated for 16 h at room temperature. (B) GST-free target protein was eluted using PBS, pH 7.3. GST was eluted using 10 mM reduced glutathione. (C) SDS-PAGE followed by silver staining. The GST-free target protein fraction also contained a small amount of thrombin not detectable by SDS-PAGE (lane 6). The thrombin can be removed using a HiTrap Benzamidine FF (high sub) column.
4. Purification and on-column cleavage of TLP40-GST-tagged protein using GSTrap FF columns and PreScission Protease
The gene coding for TLP40 protein was subcloned into pGEX-6P-1 and transformed into E. coli BL21, and the GST-tagged proteins were purified from clarified lysates using two GSTrap FF 5 mL columns connected in series. After washing with PBS and equilibration with 50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, pH 8.0, buffer flow was stopped.
For PreScission Protease digestion, 2 units of enzyme/100 µg of bound GST-tagged protein (diluted in 50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, pH 8.0) was manually injected into the columns. Following injection, the columns were closed, sealed, and incubated for 12 to 16 h at 4 °C.
Prior to elution, a 1 mL GSTrap FF column was connected downstream to the GSTrap FF proteolytic cleavage columns to capture any released GST, uncleaved GST-tagged protein, and unbound PreScission Protease, whereas the cleaved protein was directly eluted.
After the target protein had been eluted, GST, unbound GST-tagged protein, and PreScission Protease were eluted with reduced glutathione (Figure 5.6A). SDS-PAGE analysis of various fractions showed isolation of highly pure TLP40 after on-column cleavage (Figure 5.6B).
This application is reproduced with kind permission of Dr. Darcy Birse, University of Stockholm, Sweden.
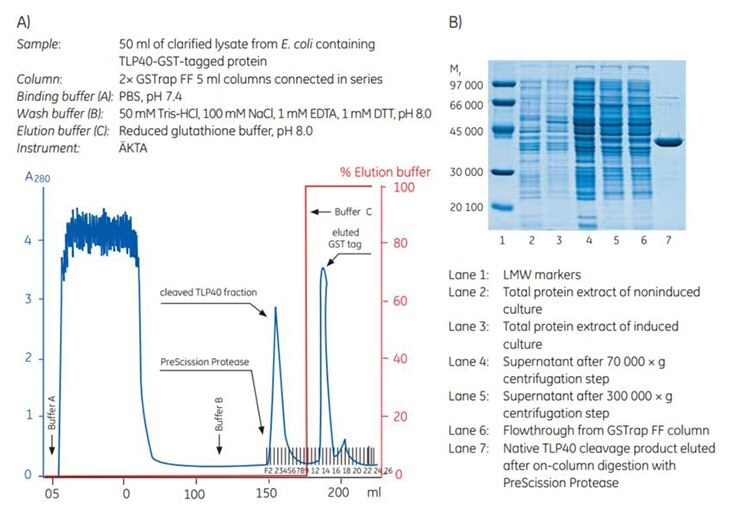
Figure 5.6. Purification and SDS-PAGE analysis of TLP40-GST-tagged protein. A) Purification and on-column cleavage of tagged protein using GSTrap FF 5 mL and PreScission Protease in combination with ÄKTA chromatography system. The flow rate for sample loading and injecting the protease were 1 mL/min and 5 to 7 mL/min, respectively. B) Fractions from the purification steps were analyzed by SDS-PAGE using a 3.5% to 12% polyacrylamide gel. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue.
如要继续阅读,请登录或创建帐户。
暂无帐户?