Bacterial Genomic Miniprep Kit
For purification of genomic DNA from a variety of cultured bacteria
Description
Our GenElute Bacterial Genomic Kit provides a simple and convenient technique to isolate high quality DNA from both Gram negative (Figure 1) and Gram positive bacteria (Figure 2). This kit combines the advantages of a silica-based system with a microspin format, eliminating the need for expensive resins and hazardous organic compounds. Bacteria are first incubated with the appropriate enzymes to ensure efficient cell lysis and DNA release from the cells.
Quick look
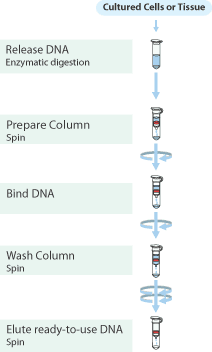
Procedure
Bacteria are first incubated with the appropriate enzymes to ensure efficient cell lysis and DNA release from the cells. The bacteria are then lysed in a chaotropic salt-containing solution. DNA is bound to the silica-based membrane and the remaining lysate is removed by centrifugation. After washing to remove contaminants, the DNA is eluted with buffer into a collection tube. Eluted DNA can be up to 50 kb in length (Figure 3) and is suitable for downstream applications such as restriction endonuclease digestions, PCR, and Southern blots.
The GenElute Bacterial Genomic DNA Kit contains all of the reagents needed to purify genomic DNA from Gram negative bacteria (Figure 3). However lysozyme (Product No. L7651), which must be purchased separately, is needed for most Gram positive bacteria to thoroughly lyse the thick peptidoglycan cell walls. A Gram positive Lysis Solution is provided with each GenElute Kit as a diluent for preparing the lysozyme stock solution.
Features and Benefits
- Protocols provided for Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria
- Purified DNA has an A260/A280ratio between 1.6 and 1.9
- Typical DNA yields of 15 µg-20 µg (See Table 1)
- Lysozyme diluent & RNase A Solution provided for added convenience
Storage: Room Temperature
R: 22-36/37/38-42 S: 26-36
Order Information |
|---|
* Values adjusted for dilution factor.
** Based on performing two 200 µl elutions.
*** Lysozyme Solution was supplemented with 250 units/ml of Mutanolysin (Product No. M9901).
**** Lysozyme Solution was supplemented with 200 units/ml of Lysostaphin (Product No. L7386).
Comparison of Gram(–) bacteria genomic DNA isolation kits.
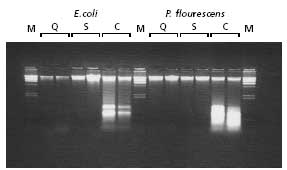
Figure 1.Agarose gel analysis of genomic DNA isolated from the indicated Gram negative bacteria prepared using the GenElute Bacterial Genomic DNA Kit versus kits from other suppliers. Equal proportions of DNA were resolved on a 1%, 1X TBE agarose gel. The Lambda Hind III ladder (Product No. D9780) was used as a size standard (M).
Comparison of Gram(+) bacteria genomic DNA isolation kits.
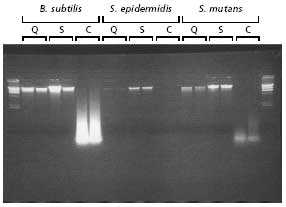
Figure 2.Agarose gel analysis of genomic DNA isolated from the indicated Gram(+) bacteria prepared using the GenElute Bacterial Genomic DNA Kit versus kits from other suppliers. Equal proportions of DNA were resolved on a 1%, 1X TBE agarose gel. The Lambda Hind III ladder (Product No. D9780) was used as a size standard.
Pulse Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) of bacterial DNA.

Figure 3.Purified genomic DNA was isolated from various bacterial species using the GenElute Bacterial Genomic DNA kit. A 1 µg aliquot of DNA from each respective bacterial sample was resolved on a 1% agarose gel in 0.5X TBE at 150 volts for 16 hours using a BioRad CHEF DRII system. The initial pulse time was 2 seconds, the final pulse time was 13 seconds, the start ratio was 1.0, pump speed was set at 70, and PFGE was carried out at 4 °C. Marker (M) represents the 0.1-200 kb Pulse marker (Product No. D2291).
Lysozyme may dissolve more readily by pipetting the mixture up and down as opposed to vortexing. This also reduces foaming that may
occur from vortexing.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?