A6255
α-Amylase from porcine pancreas
PMSF Treated, Type I-A, saline suspension, ≥1000 units/mg protein (E1%/280)
Synonym(s):
β-N-acetylglucosaminidase porcine placenta, PPA, al1,4 glucan-4-glucanohydrolase,, porcine pancreas α-amylase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Porcine pancreas
Quality Level
type
Type I-A
form
saline suspension
specific activity
≥1000 units/mg protein (E1%/280)
mol wt
51-54 kDa
greener alternative product characteristics
Waste Prevention
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
greener alternative category
, Enabling
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
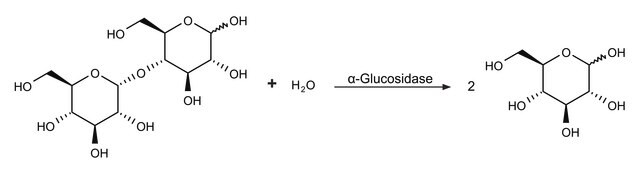
α-Amylase isolated from porcine pancreas is a glycoprotein. It is a single polypeptide chain of ~475 residues containing two SH groups and four disulfide bridges and a tightly bound Ca2+ necessary for stability. Chloride ions are necessary for activity and stability. The pH range for activity is 5.5 to 8.0, with the pH optimum at 7.
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Physical form
Preparation Note
Other Notes
inhibitor
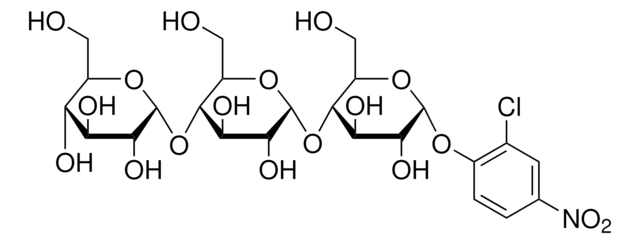
substrate
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service