C7081
WY-14643
Synonym(s):
4-Chloro-6-(2,3-xylidino)-2-pyrimidinylthioacetic acid, Pirinixic acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
powder
SMILES string
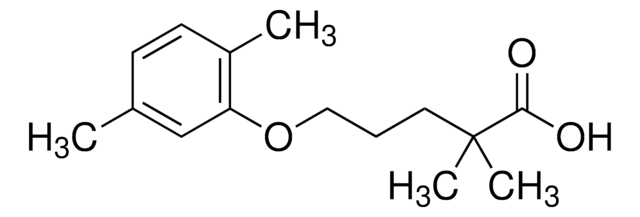
CC1=C(C)C=CC=C1NC2=NC(SCC(O)=O)=NC(Cl)=C2
InChI
1S/C14H14ClN3O2S/c1-8-4-3-5-10(9(8)2)16-12-6-11(15)17-14(18-12)21-7-13(19)20/h3-6H,7H2,1-2H3,(H,19,20)(H,16,17,18)
InChI key
SZRPDCCEHVWOJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
human ... PPARA(5465) , PPARD(5467) , PPARG(5468)
mouse ... Ppara(19013)
rat ... Ppara(25747)
General description
Application
- as a positive control for transfection and luciferase assay
- to stimulate bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDM) for autophagic flux analysis
- to analyze the regulation of fatty acid metabolism-immune nexus (FAMIN) expression in cell culture
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Carc. 1B - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
target_organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
ppe
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service