D7250
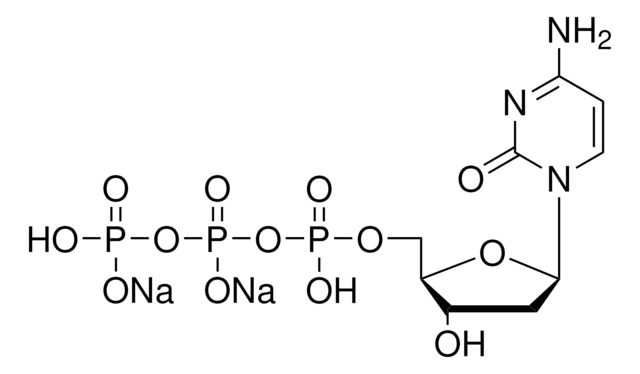
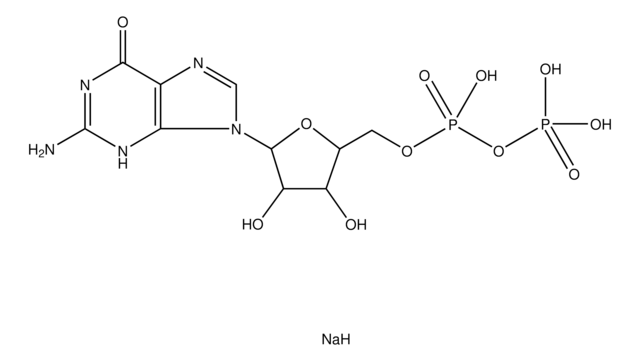
2′-Deoxycytidine 5′-diphosphate sodium salt
≥96%
Synonim(y):
dCDP
About This Item
Próba
≥96%
Postać
powder
temp. przechowywania
−20°C
ciąg SMILES
O.[Na].NC1=NC(=O)N(C=C1)C2CC(O)C(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(O)=O)O2
InChI
1S/C9H15N3O10P2.Na.H2O.H/c10-7-1-2-12(9(14)11-7)8-3-5(13)6(21-8)4-20-24(18,19)22-23(15,16)17;;;/h1-2,5-6,8,13H,3-4H2,(H,18,19)(H2,10,11,14)(H2,15,16,17);;1H2;
Klucz InChI
MNOALMYIRLFAQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Powiązane kategorie
Zastosowanie
Hasło ostrzegawcze
Danger
Zwroty wskazujące rodzaj zagrożenia
Zwroty wskazujące środki ostrożności
Klasyfikacja zagrożeń
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organy docelowe
Respiratory system
Kod klasy składowania
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 3
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Klienci oglądali również te produkty
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej