AB5032
Anti-Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule Antibody
Chemicon®, from rabbit
Synonim(y):
CD56 antigen, antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody 5.1H11
About This Item
Polecane produkty
pochodzenie biologiczne
rabbit
Poziom jakości
forma przeciwciała
affinity purified immunoglobulin
rodzaj przeciwciała
primary antibodies
klon
polyclonal
oczyszczone przez
affinity chromatography
reaktywność gatunkowa
mouse, rat, chicken, human
producent / nazwa handlowa
Chemicon®
metody
ELISA: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
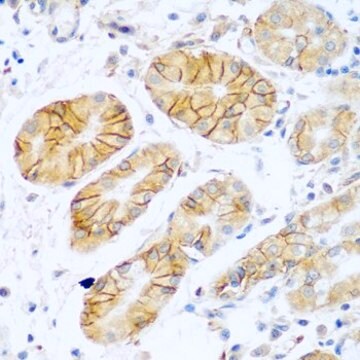
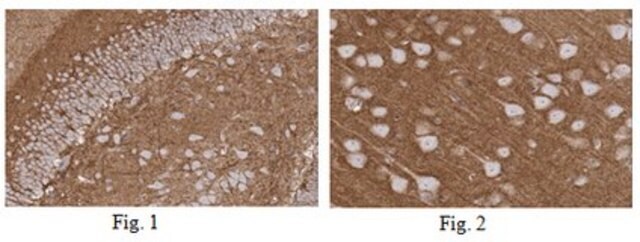
immunohistochemistry: suitable
western blot: suitable
numer dostępu NCBI
numer dostępu UniProt
Warunki transportu
dry ice
docelowa modyfikacja potranslacyjna
unmodified
informacje o genach
human ... NCAM1(4684)
Opis ogólny
Specyficzność
Immunogen
Zastosowanie
A previous lot was shown to work with a wide range of fixatives. Will detect chicken NCAM using a concentration of 1 μg/mL and mouse NCAM using a concentration of 2 μg/mL.
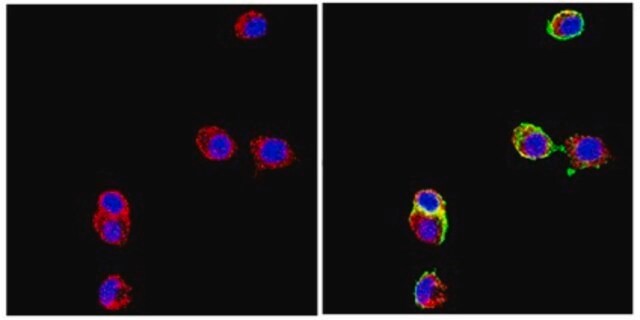
Immunofluorescence:
A previous lot of this antibody was used in Immunofluorescence.
Function blocking:
A previous lot of this antibody was used in Function blocking.
ELISA:
0.3 μg/mL of a previous lot was used.
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Neuroscience
Growth Cones & Axon Guidance
Jakość
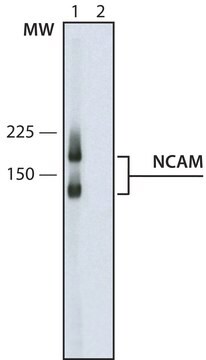
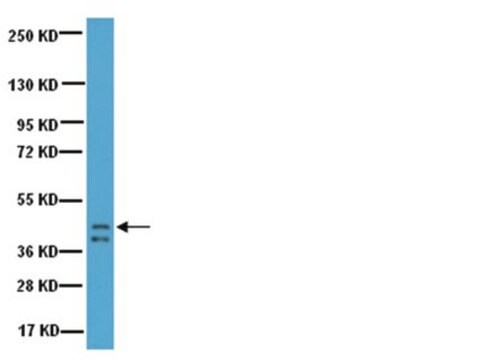
Western Blot Analysis: 1:1000 dilution of this lot detected NCAM on 10 μg of mouse brain lysate.
Opis wartości docelowych
Postać fizyczna
Przechowywanie i stabilność
Handling Recommendations:
Upon first thaw, and prior to removing the cap, centrifuge the vial and gently mix the solution. Aliquot into microcentrifuge tubes and store at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles, which may damage IgG and affect product performance.
Komentarz do analizy
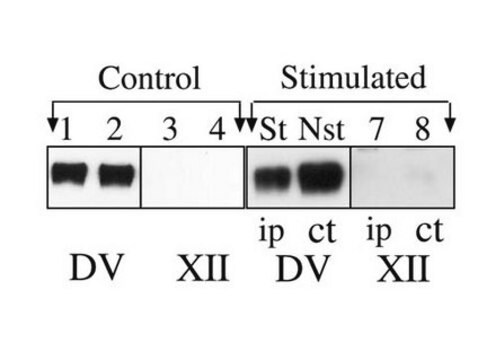
Neuraminidase-treated mouse brain membrane.
Inne uwagi
Informacje prawne
Oświadczenie o zrzeczeniu się odpowiedzialności
Not finding the right product?
Try our Narzędzie selektora produktów.
Kod klasy składowania
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Klasa zagrożenia wodnego (WGK)
WGK 2
Temperatura zapłonu (°F)
Not applicable
Temperatura zapłonu (°C)
Not applicable
Certyfikaty analizy (CoA)
Poszukaj Certyfikaty analizy (CoA), wpisując numer partii/serii produktów. Numery serii i partii można znaleźć na etykiecie produktu po słowach „seria” lub „partia”.
Masz już ten produkt?
Dokumenty związane z niedawno zakupionymi produktami zostały zamieszczone w Bibliotece dokumentów.
Nasz zespół naukowców ma doświadczenie we wszystkich obszarach badań, w tym w naukach przyrodniczych, materiałoznawstwie, syntezie chemicznej, chromatografii, analityce i wielu innych dziedzinach.
Skontaktuj się z zespołem ds. pomocy technicznej