186252
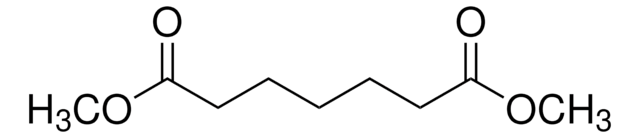
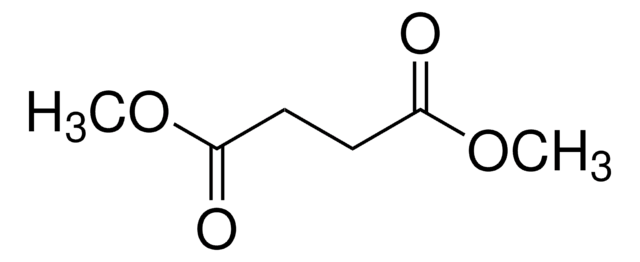
Dimethyl adipate
≥99%
Synonym(s):
Adipinic acid dimethyl ester, Dimethyl 1,6-hexanedioate, Dimethyl hexanedioate
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
0.06 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Assay
≥99%
form
liquid
autoignition temp.
680 °F
expl. lim.
8.1 %
refractive index
n20/D 1.428 (lit.)
bp
109-110 °C/14 mmHg (lit.)
mp
8 °C (lit.)
density
1.062 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
COC(=O)CCCCC(=O)OC
InChI
1S/C8H14O4/c1-11-7(9)5-3-4-6-8(10)12-2/h3-6H2,1-2H3
InChI key
UDSFAEKRVUSQDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- Micro/nanoencapsulation for cool thermal energy storage: Dimethyl adipate has been encapsulated into a polymer shell, improving its thermal properties and making it suitable for cool thermal energy storage applications (Trivedi & Parameshwaran, 2022).
- Sustainable production via non-heme iron (III) catalysis: A method for producing dimethyl adipate through oxidative cleavage of catechol using non-heme iron (III) catalysts highlights an environmentally friendly approach (Jastrzebski et al., 2015).
- Boosted nitrilation for adiponitrile production: The development of bimetallic oxide catalysts for the nitrilation of dimethyl adipate to adiponitrile shows enhanced activity and selectivity, important for industrial applications (Guo et al., 2023).
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
230.0 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
110 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service