Assay Procedure for Cholesterol Esterase
Cholesterol esterase is a reversible enzyme that can hydrolyze or synthesize fatty acid esters of cholesterol and other sterols. It also hydrolyzes tri-, di-, and mono-acylglycerols, phospholipids, lysophospholipids, and ceramide. Cholesterol esterase may have multiple functions in lipid and lipoprotein metabolism, and atherosclerosis.
PRINCIPLE
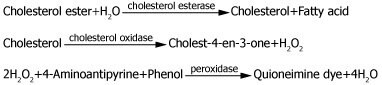
The appearance of quinoneimine dye formed when coupled with 4-aminoantipyrine and phenol is measured at 500 nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition
One unit causes the formation of one micromole of hydrogen peroxide (half a micromole of quinoneimine dye) per minute under the conditions described below.
Method
Procedure
- Prepare the following working solution (50 tests) in a brown bottle.
75 mL Buffer solution (A)
50 mL Substrate solution (B)
2.5 mL 4-AA solution (C)
5.0 mL Phenol solution (D)
5.0 mL POD solution (E)
Concentration in assay mixture |
|---|
- Pipette 2.75 mL of working solution into a cuvette (d=1.0 cm) and equilibrate at 37 ℃ for about 5 minutes. Add 0.1 mL of COD solution (F), mix and keep at 37 ℃ for another 2 minutes.
- Add 0.1 mL of the enzyme solution* and mix with gentle inversion.
- Record the increase in optical density at 500nm against water for 3 to 4 minutes in a spectrophotometer thermostated at 37 ℃, and calculate the ΔOD per minute from the initial linear portion of the curve (ΔOD test).
At the same time, measure the blank rate (ΔOD blank) using the same method as the test except that the enzyme diluent (G) is added instead of the enzyme solution.
* Dissolve the enzyme preparation in ice-cold enzyme diluent (G), and dilute to 0.08-0.22U/mL with the same buffer, immediately before assay.
Calculation
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula:

To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?