Global DNA Methylation Quantification
Savita Bagga
BioFiles v7 n3, 2012, 6
The overall degree of methylation of a genome can be a useful measure of global regulatory changes. Measurement of this parameter is usually performed after complete digestion to the single base and then analyzed using HPLC or mass spectrophotometry.
Global DNA Modification Kit
The Global DNA Modification Kit (MDQ1), allows the researcher to monitor DNA methylation using a format similar to a sandwich ELISA assay. This is a format more friendly to biological researchers, and is the first of its kind on the market.
Features and Benefits
- ELISA-Based Format
– Procedure completes in four easy-to-follow steps
– All reagents supplied, including methylated DNA control
- Quickly Measures Changes in DNA Methylation
– Detection limit is 5 ng of fully methylated DNA
– Input DNA may be as low as 10–200 ng
- Complete, Flexible, and Fast
– Procedure complete in 3.5 hours
– 96-well format allows option of studying single samples or high-throughput studies
- Extended Range of DNA Sample Sources
– May be used with DNA from cells, tissues, plasma, and other body fluids
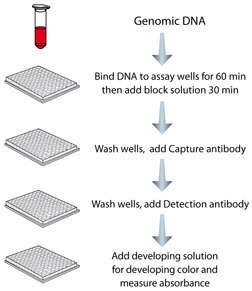
Step-wise protocol for using MDQ1.
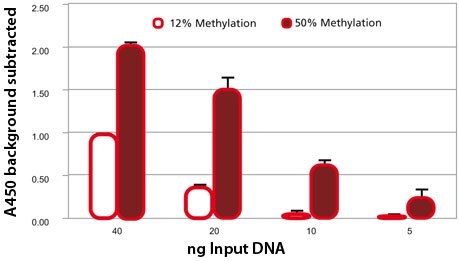
Comparison of two differently methylated lots of DNA with MDQ1. Methylation status of two lots of Sss I treated DNA was measured by LC-MS. Varying amounts of DNA was also analyzed via the MDQ1 kit. As demonstrated by the graph, the difference in methylation states can easily be detected and the signal generated is proportional to the amount of DNA used in the procedure.
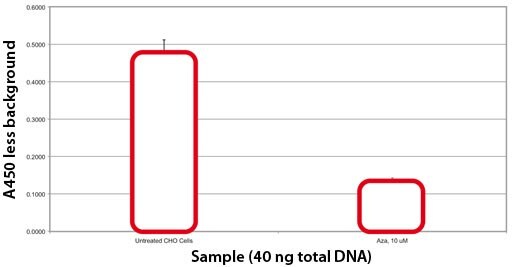
Effect of Azacytadine on CHO Cell Global Methylation. Azacytadine, a known demethylating agent, was added directly to culture medium. Cells were harvested after 48 hours. DNA was isolated using GenEluteTM and global methylation was measured. 40 ng of DNA from treated and non-treated CHO cells was analyzed.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?