DIOP is one of the first chiral ligands used for asymmetric hydrogenation catalysis. DIOP can be synthesized in four simple steps from tartaric acid. Chelation with a rhodium complex generates an optically active catalyst active in hydrogenation. To demonstrate the activity of DIOP, Kagan and Dang conducted the asymmetric hydrogenation of a variety of alkenes.1 Optical yields of up to 72% were obtained with substrate to catalyst ratio of up to 200:1 (Scheme 1).
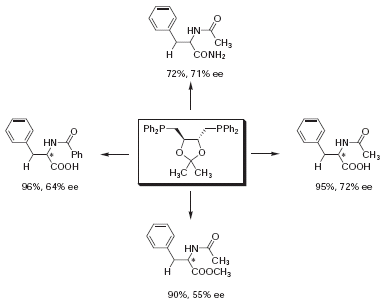
Scheme 1.
Materials
Loading
References
1.
Dang TP, Kagan HB. 1971. The asymmetric synthesis of hydratropic acid and amino-acids by homogeneous catalytic hydrogenation. J. Chem. Soc. D.(10):481. https://doi.org/10.1039/c29710000481
Sign In To Continue
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?