GC Analysis of Bacterial Acid Methyl Esters (BAMEs) on SUPELCOWAX 10 (15 m x 0.10 mm I.D., 0.10 μm), Fast GC Analysis
Materiales
Analytical column
Standard
Bacterial Acid Methyl Ester (BAME) Mix
solution (10 mg/mL total concentration in methyl caproate), analytical standardCONDITIONS
column
SUPELCOWAX 10, 15 m x 0.10 mm I.D., 0.10 μm (24343)
oven
80°C (0.3 min), 30 °C/min to 180 °C (0.5 min), 10 °C/min to 200 °C (1 min)
inj. temp.
250 °C
detector
FID, 250 °C
carrier gas
hydrogen, 45 cm/sec, constant
injection
0.1 μL 200:1 split
liner
2 mm I.D., straight
sample
bacterial methyl ester standards in methyl caproate, 10 mg/mL (47080-U)
Descripción
Analysis Note
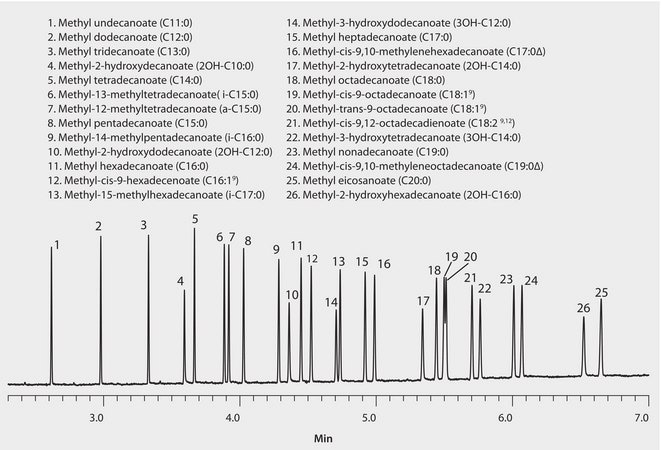
Food-borne microbial pathogens can cause illness in humans. Because each bacterium has a unique cellular fatty acid profile, GC analysis can be used to help with identification. Analysis is performed following derivatization of cellular fatty acids to methyl esters. These are called bacterial acid methyl esters (BAMEs) instead of fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) to signify the bacterial source. The chromatogram shown is the analysis of a standard mix containing 26 BAME compounds. The polar nature of the column, along with the use of Fast GC column dimensions and instrument conditions, allows good peak shape and resolution in just 7 minutes.
Legal Information
null