E9783
p3XFLAG-CMV™-9 Expression Vector
Shuttle vector for transient or stable expression of secreted N-terminal 3xFLAG fusion proteins
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
tag
3X FLAG tagged
grade
for molecular biology
form
buffered aqueous solution
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
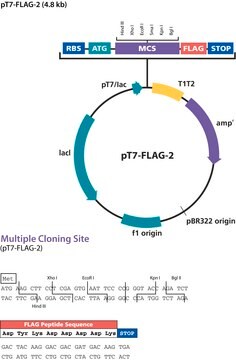
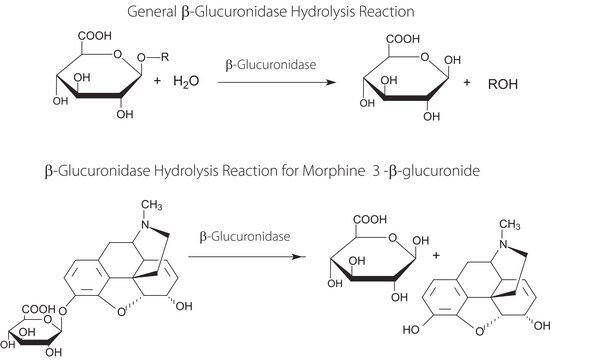
The p3XFLAG-CMV™-9 Expression Vector is a 6.4 kb derivative of pCMV5 used to establish transient or stable expression of secreted N-terminal 3XFLAG™ fusion proteins in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG?epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa- Asp) upstream of the multiple cloning region. This results in increased detection sensitivity using ANTIFLAG M2 antibody. The third epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein.
p3XFLAG-CMV-9 expression vector is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication and genomic integration is optimal when using an SV40 T antigen expressing host, such as COS cells. A related vector, p3XFLAG-CMV-3, has been used for stable transfection of HEK 293 cells. Efficiency of replication and genomic integration is optimal when using an SV40 T antigen-expressing host.
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.2 kb derivative of pCMV5 used for transient intracellular expression of N-terminal 3XFLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) upstream of the multiple cloning region. This results in increased detection sensitivity using ANTI-FLAG M2 antibody. The third FLAG epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein.
Vector Maps and Sequences
p3XFLAG-CMV-9 expression vector is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication and genomic integration is optimal when using an SV40 T antigen expressing host, such as COS cells. A related vector, p3XFLAG-CMV-3, has been used for stable transfection of HEK 293 cells. Efficiency of replication and genomic integration is optimal when using an SV40 T antigen-expressing host.
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.2 kb derivative of pCMV5 used for transient intracellular expression of N-terminal 3XFLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) upstream of the multiple cloning region. This results in increased detection sensitivity using ANTI-FLAG M2 antibody. The third FLAG epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein.
Vector Maps and Sequences
Components
- p3XFLAG-CMV™-9 Expression Vector 20 μg (E4276) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
- p3XFLAG-CMV™-7-BAP Control Plasmid 20 μg (C7472) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
Principle
The promoter-regulatory region of the human cytomegalovirus drives transcription of FLAG®-fusion constructs. The preprotrypsin leader sequence precedes the FLAG® sequence. The aminoglycoside phosphotransferase II gene (Neo-r) confers resistance to aminoglycosides such as G418 allowing for selection of stable transfectants.
Legal Information
This product is covered by the following patents owned by Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC: US6,379,903, US7,094,548, JP4405125,EP1220933, CA2386471 and AU774216.
3xFLAG is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
p3xFLAG-CMV is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Shuntaro Oniki et al.
Cancer research, 66(12), 6395-6404 (2006-06-17)
Recent studies revealed that two novel interleukin (IL)-12-related cytokines, IL-23 and IL-27, have potent antitumor activities. However, the antitumor effects were mainly evaluated in relatively highly immunogenic tumors and have not been fully evaluated against nonimmunogenic or poorly immunogenic tumors.
Sylvie Brassart-Pasco et al.
PloS one, 7(4), e29587-e29587 (2012-04-28)
NC1 domains from α1, α2, α3 and α6(IV) collagen chains were shown to exert anti-tumor or anti-angiogenic activities, whereas the NC1 domain of the α4(IV) chain did not show such activities so far. We demonstrate in the present paper that
Alexander David Barrow et al.
The Journal of clinical investigation, 121(9), 3505-3516 (2011-08-16)
Osteoclasts are terminally differentiated leukocytes that erode the mineralized bone matrix. Osteoclastogenesis requires costimulatory receptor signaling through adaptors containing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs), such as Fc receptor common γ (FcRγ) and DNAX-activating protein of 12 kDa. Identification of these
Annapoorani Chockalingam et al.
European journal of immunology, 41(8), 2176-2184 (2011-05-24)
Nucleic acid structures are highly conserved through evolution and when self nucleic acids are aberrantly detected by toll-like receptors (TLRs) they contribute to autoimmune disease. For this reason, multiple regulatory mechanisms exist to prevent immune responses to self nucleic acids.
Shuling Fan et al.
The Journal of cell biology, 178(3), 387-398 (2007-07-25)
The Crumbs family of apical transmembrane proteins regulates apicobasal polarity via protein interactions with a conserved C-terminal sequence, ERLI. However, one of the mammalian Crumbs proteins, Crumbs3 (CRB3) has an alternate splice form with a novel C-terminal sequence ending in
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service