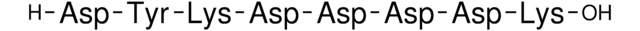E9283
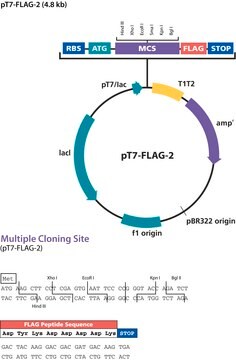
p3xFLAG-Myc-CMV™-24 Expression Vector
Shuttle vector for transient intracellular expression of dual tagged N-terminal Met-3xFLAG and C-terminal c-myc fusion proteins
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
Recommended Products
tag
3X FLAG tagged
c-Myc tagged (C-terminal)
grade
for molecular biology
form
buffered aqueous solution
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
The p3XFLAG-Myc-CMV™-24 Expression Vector is a 4.7 kb derivative of pCMV5 used to establish transient, intracellular dual-tagged N-terminal Met-3XFLAG™ and C-terminal c-myc fusion proteins in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) and a c-myc epitope (EQKLISEEDL) upstream and downstream of the multiple cloning sites, respectively. The third FLAG epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein. The incorporation of 3XFLAG in the expression vector results in increased detection sensitivity using ANTI-FLAG M2 antibody.
p3XFLAG-Myc-CMV-24 Expression Vector is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication is optimal when using an SV40 T antigen expressing host.
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.2 kb derivative of pCMV5 used for transient intracellular expression of N-terminal 3X-FLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) upstream of the multiple cloning region. This results in increased detection sensitivity using ANTI-FLAG M2 antibody. The third FLAG epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein.
FLAG® Vector Maps and Sequences portal.
p3XFLAG-Myc-CMV-24 Expression Vector is a shuttle vector for E. coli and mammalian cells. Efficiency of replication is optimal when using an SV40 T antigen expressing host.
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7-BAP Control Plasmid is a 6.2 kb derivative of pCMV5 used for transient intracellular expression of N-terminal 3X-FLAG bacterial alkaline phosphatase fusion protein in mammalian cells. The vector encodes three adjacent FLAG epitopes (Asp-Tyr-Lys-Xaa-Xaa-Asp) upstream of the multiple cloning region. This results in increased detection sensitivity using ANTI-FLAG M2 antibody. The third FLAG epitope includes the enterokinase recognition sequence, allowing cleavage of the 3XFLAG peptide from the purified fusion protein.
FLAG® Vector Maps and Sequences portal.
Application
The p3XFLAG-Myc-CMV™-24 Expression Vector is suitable for expression of C-terminal c-myc N-terminal Met-3XFLAG™ fusion proteins in mammalian cells.
Components
- p3XFLAG-Myc-CMV™-24 Expression Vector 20 μg (E6151) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
- p3XFLAG-CMV™-7-BAP Control Plasmid 20 μg (C7472) is supplied as 0.5 mg/ml in 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) with 1 mM EDTA.
Principle
The promoter-regulatory region of the human cytomegalovirus drives transcription of FLAG® and c-myc fusion constructs.
Legal Information
This product is covered by the following patents owned by Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC: US6,379,903, US7,094,548, JP4405125,EP1220933, CA2386471 and AU774216.
3xFLAG is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
FLAG is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
p3xFLAG-CMV is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
p3xFLAG-Myc-CMV is a trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Sean P Cregan et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 24(44), 10003-10012 (2004-11-05)
The p53 tumor suppressor gene has been implicated in the regulation of apoptosis in a number of different neuronal death paradigms. Because of the importance of p53 in neuronal injury, we questioned the mechanism underlying p53-mediated apoptosis in neurons. Using
Heena Dey et al.
BMC cell biology, 13, 27-27 (2012-11-01)
We previously demonstrated that p68 phosphorylation at threonine residues correlates with cancer cell apoptosis under the treatments of TNF-α and TRAIL (Yang, L. Mol Cancer Res Vol 3, pp 355-63 2005). In this report, we characterized the role of p68
Huizhi Wang et al.
Oncogenesis, 9(8), 76-76 (2020-08-28)
Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) has been characterized as an oncogene in several types of cancer. However, its precise role in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains unclear. Hence, this study aimed to evaluate the potential role of MeCP2 in pancreatic cancer
Jesse D Roberts et al.
American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology, 293(4), L903-L912 (2007-07-03)
Nitric oxide modulates vascular smooth muscle cell (SMC) cytoskeletal kinetics and phenotype, in part, by stimulating cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (PKGI). To identify molecular targets of PKGI, an interaction trap screen in yeast was performed using a cDNA encoding the
Ko Momotani et al.
Circulation research, 109(9), 993-1002 (2011-09-03)
In normal and diseased vascular smooth muscle (SM), the RhoA pathway, which is activated by multiple agonists through G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), plays a central role in regulating basal tone and peripheral resistance. This occurs through inhibition of myosin light
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service