All Photos(3)
About This Item
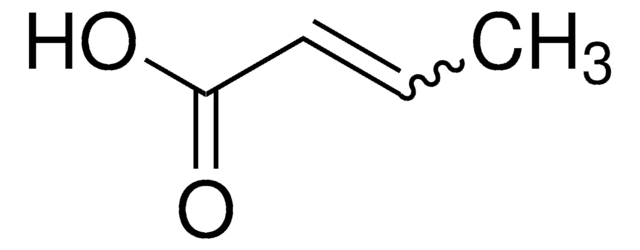
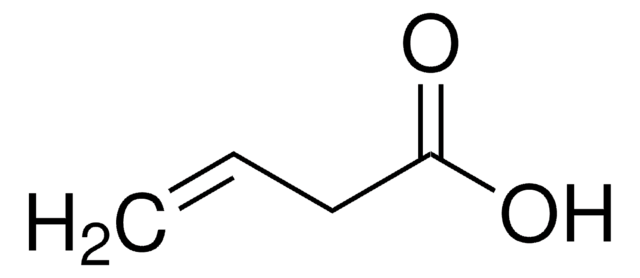
Linear Formula:
CH3C≡CCO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
84.07
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352100
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
Assay
98%
form
solid
mp
78-80 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CC#CC(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H4O2/c1-2-3-4(5)6/h1H3,(H,5,6)
InChI key
LUEHNHVFDCZTGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
The rotational spectrum of 2-butynoic acid was measured by pulsed supersonic-jet Fourier transform microwave spectroscopy.
Application
2-Butynoic acid was employed as synthon in a variety of reactions, including cycloacylation of phenols to flavones and chromones, and cyclization to γ-butyrolactones. It was also used in synthesis of Z-trisubstituted olefins via γ-alkylation.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Almost free methyl top internal rotation: Rotational spectrum of 2-butynoic acid.
Ilyushin V, et al.
Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy, 267(1), 186-190 (2011)
gamma.-Alkylation of 2-butynoic acid. Route to controlled prenol homologation.
Pitzele BS, et al.
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 40(2), 269-270 (1975)
Jie Chen et al.
The journal of physical chemistry. B, 112(26), 7794-7802 (2008-06-06)
The solution behavior of a model compound, tetrolic acid (TTA), is studied via molecular dynamics simulations in four organic solvents. The results suggest that strong interactions between TTA and solvent molecules (ethanol or dioxane) prevent the formation of carboxylic acid
S Parveen et al.
Chemical communications (Cambridge, England), (12)(12), 1531-1533 (2005-03-17)
The application of FTIR spectroscopy to concentrated solutions of tetrolic acid shows, for the first time, a direct relationship between molecular self association in solution and H-bonded motifs in the subsequently crystallised solid phases.
I A Mjör et al.
Journal of dental research, 61(8), 967-972 (1982-08-01)
Adhesive bonding of resins to dentin surfaces requires the removal of the layer of debris caused by the cutting. Certain isotonic acidic solutions can do this rapidly. Five solutions were evaluated using cell cultures and pulp studies in monkeys. At
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service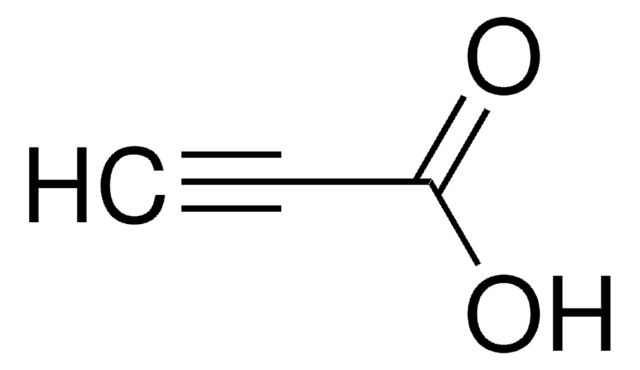

![1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/120/564/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb/640/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb.png)