N9914
Polynucleotide phosphorylase from Synechocystis sp.
recombinant, expressed in E. coli
Sinonimo/i:
PNPase, Polyribonucleotide Nucleotidyltransferase
About This Item
Prodotti consigliati
Origine biologica
bacterial (Synechocystis sp.)
Livello qualitativo
Ricombinante
expressed in E. coli
Descrizione
Histidine tagged
Saggio
90% (SDS-PAGE)
Forma fisica
solution
Attività specifica
≥500 units/mg protein
PM
85 kDa
tecniche
cell based assay: suitable
Compatibilità
suitable for molecular biology
applicazioni
cell analysis
Condizioni di spedizione
dry ice
Temperatura di conservazione
−70°C
Cerchi prodotti simili? Visita Guida al confronto tra prodotti
Descrizione generale
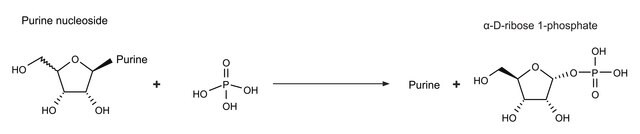
Applicazioni
Azioni biochim/fisiol
Definizione di unità
Codice della classe di stoccaggio
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe di pericolosità dell'acqua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto d’infiammabilità (°F)
Not applicable
Punto d’infiammabilità (°C)
Not applicable
Certificati d'analisi (COA)
Cerca il Certificati d'analisi (COA) digitando il numero di lotto/batch corrispondente. I numeri di lotto o di batch sono stampati sull'etichetta dei prodotti dopo la parola ‘Lotto’ o ‘Batch’.
Possiedi già questo prodotto?
I documenti relativi ai prodotti acquistati recentemente sono disponibili nell’Archivio dei documenti.
I clienti hanno visto anche
Il team dei nostri ricercatori vanta grande esperienza in tutte le aree della ricerca quali Life Science, scienza dei materiali, sintesi chimica, cromatografia, discipline analitiche, ecc..
Contatta l'Assistenza Tecnica.