T3068
Thrombin generation chromogenic substrate
≥90% (HPLC), solid
Synonym(s):
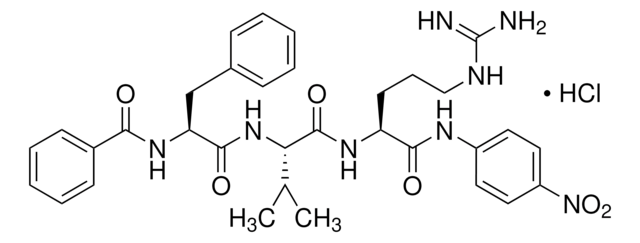
β-Ala-Gly-Arg-p-nitroanilide diacetate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C21H34N8O9
Molecular Weight:
542.54
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.32
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic (organic)
Quality Level
Assay
≥90% (HPLC)
form
solid
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
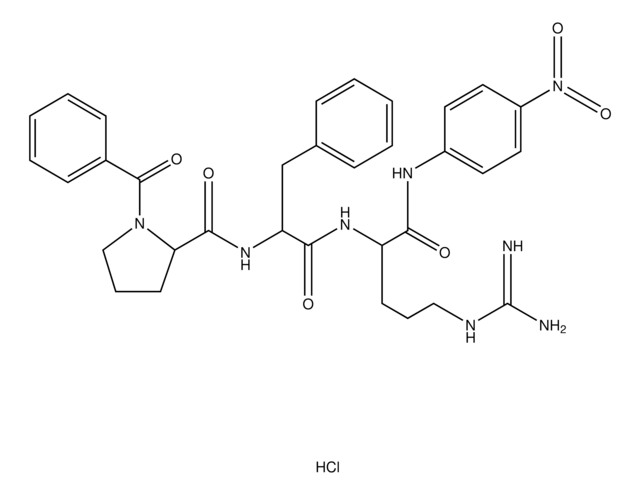
[N+](=O)([O-])c1ccc(cc1)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)CNC(=O)CCN)CCCNC(=N)N.OC(=O)C.OC(=O)C
Amino Acid Sequence
Ala-Gly-Arg-pNA
Application
Thrombin generation chromogenic substrate can be used for chromogenic assay developed through aptamer affinity capture and a subsequent enzyme reaction for detecting the thrombin in dilute human serum.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Thrombin generation chromogenic substrate also known as beta-Ala-Gly-Arg para-nitroanilide, is proteolytically cleaved by human thrombin and produces beta-Ala-Gly-Arg and p-nitroanilide. The release of p-nitroanilide is quatified for assesing the anti-thrombin activity.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Qiang Zhao et al.
Biosensors & bioelectronics, 34(1), 232-237 (2012-03-06)
A simple chromogenic assay for human alpha thrombin is developed through aptamer affinity capture and a subsequent enzyme reaction. Thrombin is captured on the aptamer-modified magnetic beads, and catalyzes the conversion of chromogenic substrates to optically measured products. The measurement
D Prasa et al.
Thrombosis and haemostasis, 78(4), 1215-1220 (1997-11-19)
A series of inhibitors of factor Xa (FXa) were investigated using the thrombin generation assay to evaluate the potency and specificity needed to efficiently block thrombin generation in activated human plasma. By inhibiting FXa the generation of thrombin in plasma
Jan Van Den Abbeele et al.
PLoS pathogens, 6(6), e1000926-e1000926 (2010-06-10)
Tsetse flies are the notorious transmitters of African trypanosomiasis, a disease caused by the Trypanosoma parasite that affects humans and livestock on the African continent. Metacyclic infection rates in natural tsetse populations with Trypanosoma brucei, including the two human-pathogenic subspecies
Jingjing Wang et al.
Frontiers in microbiology, 12, 778309-778309 (2021-12-21)
African swine fever virus (ASFV) is a large double-stranded DNA virus and causes high mortality in swine. ASFV can be transmitted by biological vectors, including soft ticks in genus Ornithodoros but not hard ticks. However, the underlying mechanisms evolved in
Ning Luan et al.
Toxins, 11(12) (2019-12-11)
Elastase is a globular glycoprotein and belongs to the chymotrypsin family. It is involved in several inflammatory cascades on the basis of cleaving the important connective tissue protein elastin, and is strictly regulated to a balance by several endogenous inhibitors.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service