P8590
Anti-CD31(PECAM-1) antibody , Mouse monoclonal
clone WM-59, purified from hybridoma cell culture
Synonym(s):
Anti-EndoCAM, Anti-GPIIA, Anti-PECA1, Anti-PECAM-1
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(1)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.41
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified from hybridoma cell culture
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
WM-59, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
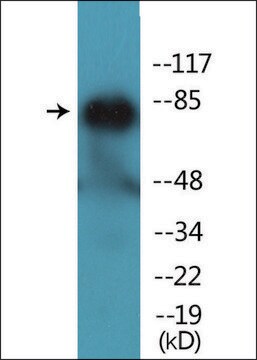
antigen 130-140 kDa
species reactivity
human
technique(s)
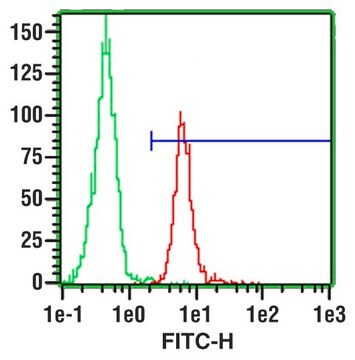
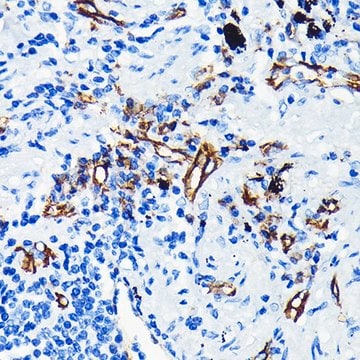
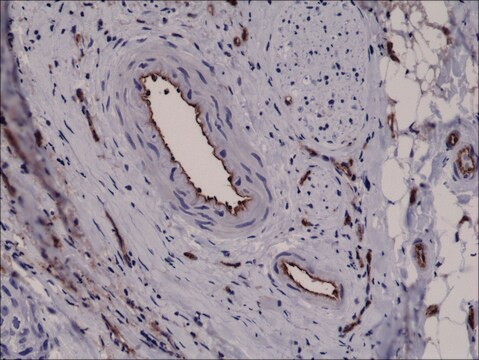
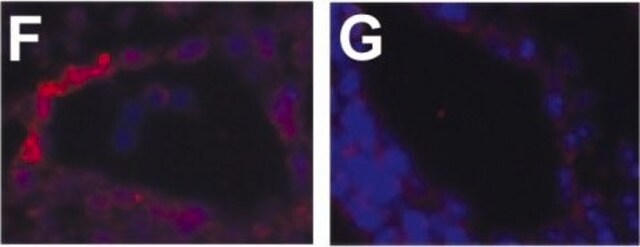
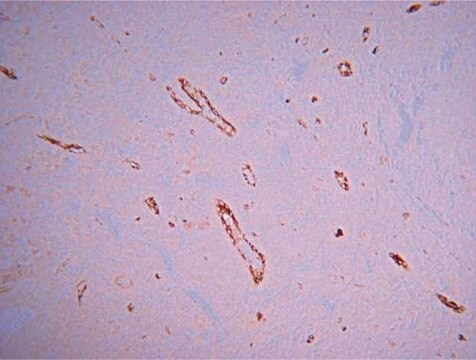
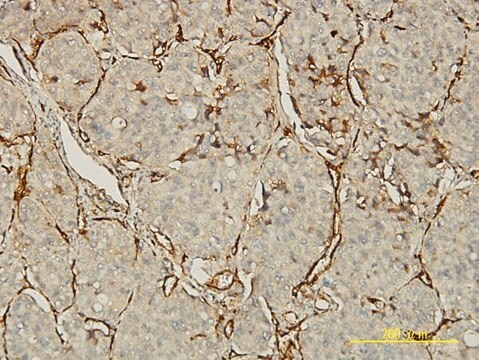
indirect immunofluorescence: 1:100 using endothelial cells in human placenta frozen sections
General description
Recognizes the CD31 (PECAM-1, endoCAM, gpIIa, hec7), human cell surface integral membrane glycoprotein. The antibody increases the rate of homotypic aggregation induced in U937 cells by TGF-β1. Its reactivity with platelets is enhanced following their washing.
5th Workshop: code No. P025
5th Workshop: code No. P025
The cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31), also known as platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM1) gene, spanning 75kb, is mapped on the long arm of human chromosome 17. This gene codes for a 130kDa protein, which belongs to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is a vital component of the endothelial cell intercellular junction. CD31 is expressed on the surface of circulating platelets, monocytes, neutrophils and selected T-cell subsets.
The human PECAM-1 antigen (Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule, CD31, endoCAM. gpIIa, hec7) is a 130-140 kD single chain integral membrane glycoprotein member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily of cell adhesion molecules. Human PECAM-1 (CD31) is expressed on platelets, myeloid cells, B lymphocytes, certain T lymphocyte cell subsets, bone marrow precursor cells and NK cells. PECAM is abundantly expressed in endothelial cells. It becomes localized to the intracellular junctions in monolayers of cultured endothelial cells. PECAM-1 (CD31) functions in homophilic and heterophilic cell-cell adhesion and cell signaling activities. It plays a major role in the transmigration of monocytes, neutrophils and NK cells between the endothelial cell junctions into the subendothelial matrix. PECAM-1 (CD31) is possibly involved in some of the interactive events taking place during cardiovascular development inflammation, thrombosis, wound healing and angiogenesis.
Specificity
Recognizes the CD31 (PECAM-1, endoCAM, gpIIa, hec7), human cell surface integral membrane glycoprotein. The antibody increases the rate of homotypic aggregation induced in U937 cells by TGF-b1. Its reactivity with platelets is enhanced following their washing.
5th Workshop: code No. P025
5th Workshop: code No. P025
Immunogen
human cell line RC-2A, originally derived from myeloid leukemia cells.
Application
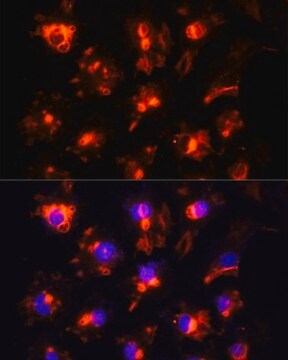
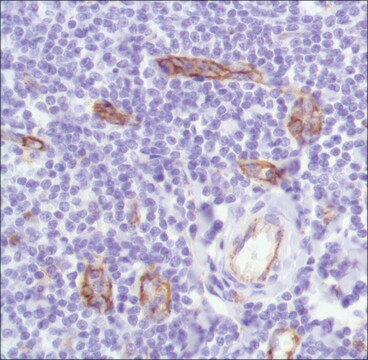
Monoclonal Anti-CD31 (PECAM-1) antibody produced in mouse has been used in immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry.
Mouse monoclonal clone WM-59 anti-human PECAM-1 (CD31) may be used for studies of PECAM-1 function in cell-cell interactions, for the detection and enumeration of CD31 cells in blood and tissues, and for the isolation of PECAM-1 by immunoaffinity chromatography. Monoclonal Anti-Human PECAM-1 (CD31) was shown to increase the rate of homotypic aggregation induced in U937 cells by TGFβ1. Its binding to platelets was reported to be enhanced following their washing and concomitant activation.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31) plays a crucial role in the adhesion cascade leading to leukocyte extravasation during the inflammatory process. The encoded protein is essential for leukocyte transmigration via intercellular junctions of vascular endothelial cells. Genetic polymorphism of the gene is associated with atherosclerotic events. CD31 is a membrane glycoprotein that facilitates both homophilic and heterophilic adhesion. CD31 is also implicated in angiogenesis.
Target description
Human CD31 (PECAM-1) is expressed on platelets, endothelial cells, myeloid cells, B lymphocytes, and certain T lymphocyte subsets. CD31 (PECAM-1) functions in homophilic and heterophilic cell-cell adhesion and cell signaling activities.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4
Preparation Note
Product filtered through a 0.2 μm filter
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Towards a Biohybrid Lung: Endothelial Cells Promote Oxygen Transfer through Gas Permeable Membranes.
Sarah Menzel et al.
BioMed research international, 2017, 5258196-5258196 (2017-09-16)
In patients with respiratory failure, extracorporeal lung support can ensure the vital gas exchange via gas permeable membranes but its application is restricted by limited long-term stability and hemocompatibility of the gas permeable membranes, which are in contact with the
Camilla Siciliano et al.
Cytotechnology, 67(1), 165-174 (2013-12-07)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are adult multipotent cells currently employed in several clinical trials due to their immunomodulating, angiogenic and repairing features. The adipose tissue is certainly considered an eligible source of MSCs. Recently, putative adipose tissue derived MSCs (ADMSCs)
Jens M Kelm et al.
Journal of biotechnology, 118(2), 213-229 (2005-06-14)
Owing to its dual impact on tissue engineering (neovascularization of tissue implants) and cancer treatment (prevention of tumor-induced vascularization), management and elucidation of vascularization phenomena remain clinical priorities. Using a variety of primary human cells and (neoplastic) cell lines assembled
Stefan Weinandy et al.
Tissue engineering. Part A, 20(13-14), 1858-1869 (2014-01-25)
A vascular supply network is essential in engineered tissues >100-200-μm thickness. To control vascular network formation in vitro, we hypothesize that capillarization can be achieved locally by using fibers to position and guide vessel-forming endothelial cells within a three-dimensional (3D)
N?Acetylcysteine, a glutathione precursor, reverts vascular dysfunction and endothelial epigenetic programming in intrauterine growth restricted guinea pigs
Herrera EA, et al.
The Journal of Physiology, 595, 1077-1092 (2017)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service