SML0995
GSK1838705A
≥98% (HPLC)
别名:
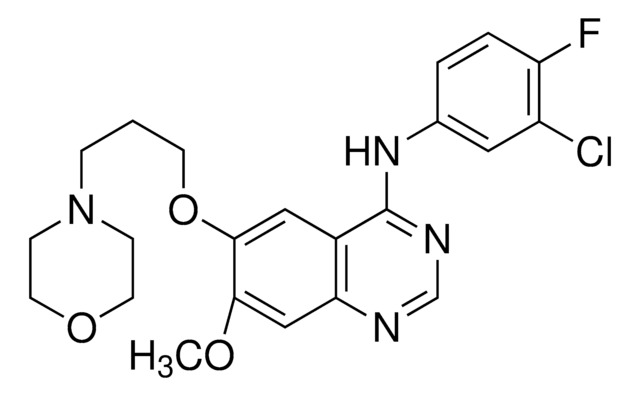
2-[[2-[[1-[(Dimethylamino)ethanoyl]-5-(methyloxy)-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-6-yl]amino]-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-6-fluoro-N-methylbenzamide, 2-[[2-[[1-[2-(Dimethylamino)acetyl]-2,3-dihydro-5-methoxy-1H-indol-6-yl]amino]-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-6-fluoro-N-methyl-benzamide
登录查看公司和协议定价
所有图片(1)
About This Item
推荐产品
品質等級
化驗
≥98% (HPLC)
形狀
powder
顏色
white to light brown
溶解度
DMSO: 20 mg/mL, clear
儲存溫度
−20°C
InChI
1S/C27H29FN8O3/c1-29-26(38)23-17(28)6-5-7-18(23)31-25-16-8-10-30-24(16)33-27(34-25)32-19-13-20-15(12-21(19)39-4)9-11-36(20)22(37)14-35(2)3/h5-8,10,12-13H,9,11,14H2,1-4H3,(H,29,38)(H3,30,31,32,33,34)
InChI 密鑰
HZTYDQRUAWIZRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
應用
GSK1838705A has been used as an insulin receptor inhibitor in Roswell Park memorial institute medium (RPMI) 1640 medium for inhibitor experiments, to prove that the induction of interleukin-1 β (IL-1β) is dependent on insulin receptor signaling.
生化/生理作用
GSK1838705A can be used to treat prostate cancer (PC). It is capable of decreasing the viability of docetaxel-sensitive and docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells. GSK1838705A can stimulate apoptosis of PC-3R cells. It is an alternative therapeutic option for crizotinib-resistant anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL).
GSK1838705A is a cell penetrant anti-tumor agent that potently inhibits the insulin-like growth factor-I receptors (IGF-IR), insulin receptors (IR) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). GSK1838705A potently inhibits cell proliferation of multiple solid and hematologic cancers and retards the growth of human tumor xenografts. GSK1838705A does not significantly affect other kinases. GSK1838705A has minimal effects on glucose homeostasis in mice.
儲存類別代碼
11 - Combustible Solids
水污染物質分類(WGK)
WGK 3
閃點(°F)
Not applicable
閃點(°C)
Not applicable
Julia Manowsky et al.
American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism, 310(11), E938-E946 (2016-04-21)
Overweight and obesity are associated with hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, and a low-grade inflammation. Although hyperinsulinemia is generally thought to result from an attempt of the β-cell to compensate for insulin resistance, there is evidence that hyperinsulinaemia itself may contribute to
Natalia J Sumi et al.
Cell chemical biology, 26(9), 1240-1252 (2019-07-02)
Despite recent successes of precision and immunotherapies there is a persisting need for novel targeted or multi-targeted approaches in complex diseases. Through a systems pharmacology approach, including phenotypic screening, chemical and phosphoproteomics, and RNA-seq, we elucidated the targets and mechanisms
我们的科学家团队拥有各种研究领域经验,包括生命科学、材料科学、化学合成、色谱、分析及许多其他领域.
联系技术服务部门