Phosphazene Bases
Introduction
Phosphazene bases are extremely strong and uncharged bases, built on a unit where a nitrogen basic center is double bonded to pentavalent phosphorus.[1,2] Through oligomerization of the peralkylated triaminoiminophosphorane unit, the basicity improves dramatically (Figure 1). In the case of the monomeric phosphazene base, its basicity is about a 2-3 units beyond the basicity range of DBU (MeCNpKBH+ 24.3) and DBN, but reaches a MeCNpKBH+ of over 40 in the case of a tetrameric P4 phosphazene base (DBU = 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene, DBN = 1,5-Diazabicyclo- [4.3.0]non-5-ene).
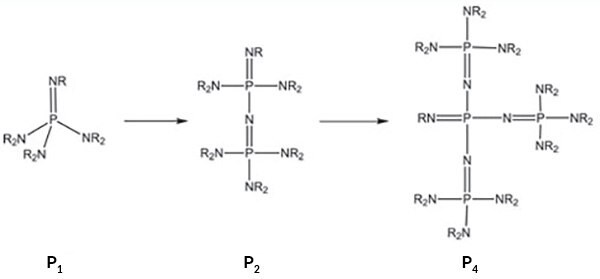
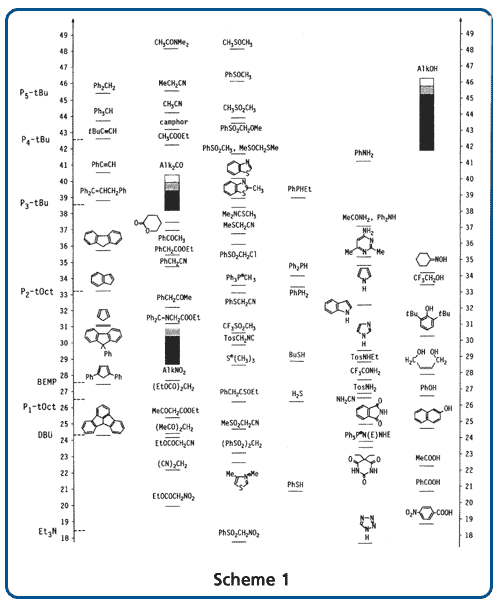
We offer these reagents as monomeric (P1 and BEMP), dimeric (P2), and tetrameric (P4) bases, with different side chains to control their sterical hindrance. Scheme 1 shows the basicity of phosphazene bases compared to other bases (in the absolute acetonitrile scale), as well as compared to the acidity of important organic compounds or classes of compounds.
- Properties of Phosphazene Bases:
- High solubility in apolar to moderately polar solvents (e.g. hexane, toluene or THF)
- Very strong solubilizing effects in appropriate weakly acidic compounds
- Remarkably stable towards electrophilic attack, O2 and hydrolysis.
- Depending on their base strength, slightly to extremely hygroscopic
- Large sterical hindrance, depending on the type of side chain
- Applications of Phosphazene Bases:
- In situ generation of highly reactive "naked" anions, e.g. for alkylation reactions or for spectroscopic investigations.
- Applicable in reactions where ionic bases cause solubility problems.
- Applicable in reactions where ionic bases are sensitive towards oxidation or acylation.
- Applicable in reactions where ionic bases result in Lewis-acid catalyzed side reactions (e.g., in aldol reactions, epoxide-opening, hydride shifts, elimination of alkoxide, polyanion-formation).
- Benefits of using Phosphazene Bases:
- Easier work-up through cleaner reactions.
- Close to quantitative recovery.
- Reaction rate enhancement.
References
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?