General description
Huntington disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by an expansion of a polyglutamine (PolyQ) domain in the protein huntingtin (htt) that leads to its aggregation into fibrils. PolyQ expansion above 35 -40 results in disease associated with htt aggregation into inclusion bodies. These expanded PolyQ repeats adopt multiple potentially toxic conformations increase atrophin-1 and huntingtin levels and abnormally sequester proteins that are essential for transcription. PolyQ domains of different lengths can display different conformations. The primary sites of neuropathology show variations between different PolyQ disorders, but usually include the cerebellum, striatum, cerebral cortex, brainstem, spinal cord, and thalamus. Huntington s disease (HD) and dentatorubral pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) display clinical similarities, but exhibit different regional pathologies. For example, in HD striatum is the most affected region whereas in DRPLA dentate nucleus of the cerebellum is more severely affected. Clone MW1 strongly binds to the expanded PolyQ of mutant Htt, but does not display any detectible binding to normal human or wild-type murine Htt. The clone MW1, which bind to the polyQ repeat in htt is reported to increase htt-induced toxicity and aggregation. (The clone MW1, which bind to the polyQ repeat in htt is reported to increased htt-induced toxicity and aggregation. (Ref.: Luthi-Carter, R et al. (2012). Hum. Mol. Gen. 11(17); 1927-1937; Legleiter, J et al. (2009). J. Biol. Chem. 284(32); 21647-21658; Ko, J et al. (2001). Brain Res. Bull. 56 (3/4); 319-329).
Specificity
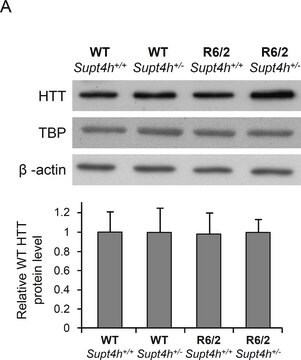
Clone MW1 specifically recognize the polyQ domain and does not react with wild-type Htt in any significant manner.
Immunogen
GST-tagged recombinant proteins expressed from two constructs containing the polyQ domain (19 repeats) and 34 amino acids of the dentatorubralpalliodoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) gene.
Application
Anti-polyQ specific, clone MW1, Cat. No. MABN2427, is a highly specific mouse monoclonal antibody that targets expanded PolyQ repeats from Huntingtin (Htt) and has been tested for use in Immunocytochemistry, Immunohistochemistry, and Western Blotting.
Research Category
Neuroscience
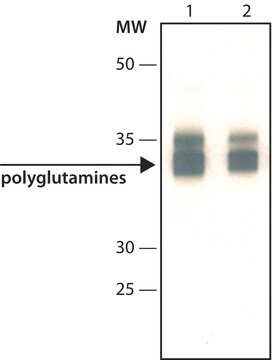
Western Blotting Analysis: A representative lot detected expanded polyQ repeats in Htt in Western Blotting applications (Ko, J., et. al. (2001). Brain Res Bull. 56(3-4):319-29; Legleiter, J., et. al. (2009). J Biol Chem. 284(32):21647-58).
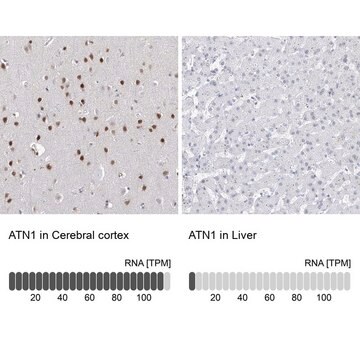
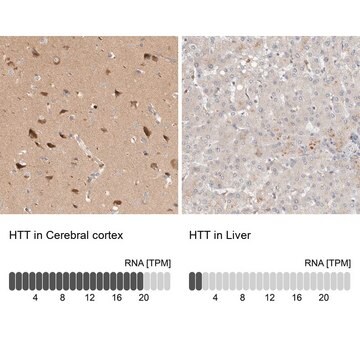
Immunohistochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected expanded polyQ repeats in Immunohistochemistry applications (Ko, J., et. al. (2001). Brain Res Bull. 56(3-4):319-29).
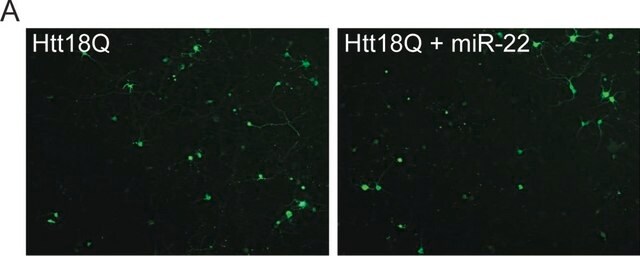
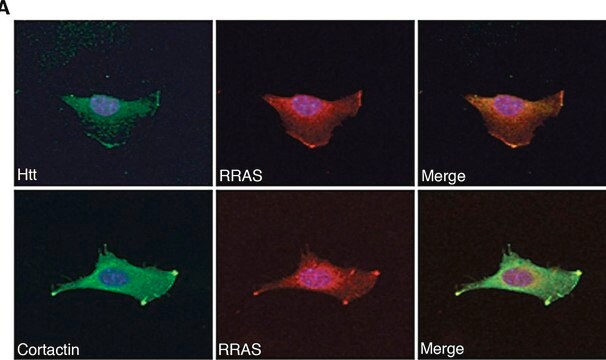
Immunocytochemistry Analysis: A representative lot detected expanded polyQ repeats in Immunocytochemistry applications (Legleiter, J., et. al. (2009). J Biol Chem. 284(32):21647-58).
Quality
Evaluated by Western Blotting in mouse brain tissue lysate.
Western Blotting Analysis: 0.5 µg/mL of this antibody detected expanded polyQ repeats in Htt in 10 µg of mouse brain tissue lysate. It does not react with normal Htt.
Target description
~350 kDa observed. Uncharacterized bands may be observed in some lysate(s).
Physical form
Format: Purified
Protein G purified
Purified mouse monoclonal antibody IgG2b in buffer containing 0.1 M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl with 0.05% sodium azide.
Storage and Stability
Stable for 1 year at 2-8°C from date of receipt.
Other Notes
Concentration: Please refer to lot specific datasheet.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.