Ago RIP to Isolate microRNA and their Targets Using Imprint® RNA Immunoprecipitation Kit
Carol Kreader, Principal R&D Scientist
The Imprint® RNA Immunoprecipitation Kit was used to co-purify human argonaute 2 (Ago2)-associated RNAs from HeLa cells, as idicated in the Technical Bulletin. To evaluate the different stringency options possible with this kit, both the Mild and the Harsh Lysis Buffers were tested, and the mild wash buffer provided in the kit was supplemented by adding 0.95% Igepal and 0.75 M NaCl to the kit’s Wash Buffer (final concentrations = 1% Igepal, 0.9 M NaCl) to prepare a more stringent, or harsh wash buffer. For each RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP), 2 million HeLa cells were lysed with either Mild or Harsh Lysis Buffer, immune precipitated with 2.5 µg of either a negative control antibody (IgG; I4131) or Ago2-specific antibody (SAB4200085), and washed with either the mild Wash Buffer included in the kit or the harsh wash buffer prepared above. Specificity of the Ago2 antibody used (SAB4200085; clone 11A9) and its suitability for immunoprecipitation were demonstrated previously by Ameyar-Zazoua et al 2012 (Nat Struc Mol Biol 19, 998; Figure 3c.), by Western Blot with and without Ago2 knockdown. Because the Ago2 antibody SAB4200085 is a monoclonal produced in rat, rabbit anti-rat (R9255; 2.5 µg) IgG was used as bridging antibody with the kit’s Protein A Magnetic Beads. Duplicate immunoprecipitations were performed for each combination of lysis and wash conditions (mild lysis/mild wash, Figure 1; mild lysis/harsh wash, Figure 2; harsh lysis/mild wash, Figure 3; harsh lysis/harsh wash, Figure 4). After purifying Ago2-associated RNA, RT-qPCR was performed with the MystiCq® microRNA cDNA Synthesis Mix (MIRRT), MystiCq® microRNA® SYBR® Green qPCR ReadyMix (MIRRM01), and MystiCq primers for 3 miRNAs, hsa-let-7c (let7c), hsa-miR125a-5p (miR125a), and hsa-miR191-5p (miR191), and 2 control small RNAs (RNU6 and SNORD48). ReadyScript® cDNA Synthesis Mix (RDRT), KiCqStart® SYBR® Green qPCR ReadyMix™ (KCQS01), and KiCqStart primers were used to detect 3 mRNAs (DICER1, MYC, and GAPDH).
All the miRNAs are expected to associate and co-immunoprecipitate with anti-Ago2. In addition, DICER1 and MYC are both published targets of let7c (Carcinogenesis 29, 2073; BMC Mol Biol 8, 79), and therefore, should be recovered with Ago 2 RIP. On the other hand, GAPDH is not known to be targeted by any miRNA in HeLa cells, and therefore, serves as a non-target negative control. While some small nuclear RNAs have been shown to associate and co-immunoprecipitate with Ago2 (Nat Struc Mol Biol 19, 998), RNU6 was not among the Ago 2-associated small RNAs reported. Furthermore, a chromatin fraction from isolated nuclei was used for RIP in the published work. With whole cell extracts, as used here, such interactions would be too rare to detect. Small RNAs originating from several small nucleolar RNAs have been reported to co-immunoprecipitate with Ago2 and function like miRNAs (Mol Cell 32, 519). However, SNORD48 was not one of the small nucleolar RNAs reported. Therefore, let7c, miR125a, miR191, DICER1, and MYC should all be detected in Ago 2 RIPs, whereas RNU6, SNORD48, and GAPDH should not.
As in Figures 1-4, the RIPs performed for this evaluation were very clean, regardless of which combination of lysis and wash conditions was used. Results for miRNAs, detected at high levels, are shown in panel A and those for non-target control RNAs and mRNAs, detected at lower levels, are in panel B of each figure. Both are expressed as % of input RNA. From 2.5 to over 105-fold more of the Ago2-target RNAs (let7c, miR125a, miR191, DICER1, and MYC) than the non-target RNAs (RNU6, SNORD48, and GAPDH) were recovered with the Ago2-specific antibody. Furthermore, target RNAs were enriched 100 to 10,000-fold in Ago 2 RIP versus nonspecific IgG, whereas non-target RNAs were enriched 0.4 to 24-fold. It should be noted that exact % input values for let-7c and miR- 125a are not reliable. Only 8% of the cell lysate was retained before immunoprecipitation and used to calculate % input, and therefore, the yields for let-7c and miR-125a were extrapolated.
Mild lysis with mild wash was the best condition for RIP with the antibodies and RNA targets used here. These conditions gave the highest yields of Ago 2 target RNAs, and sufficient discrimination between target and non-target RNAs. Harsher lysis and/or wash may be needed to distinguish target from non-target with less abundant target RNAs. The results reported here indicate that mild lysis with harsh washing could be beneficial with less abundant target RNAs. These conditions gave nearly twice the signal to noise ratio compared with other combinations of lysis and wash, and therefore, the best discrimination between target and non-target (Table 1).
The highest and lowest signal to noise ratio obtained for each combination of lysis and wash conditions is reported. To calculate the highest signal to noise ratio, yield (% input) for the most abundant Ago2 target (let7c) was divided by the yield for the least abundant non-target RNA (SNORD48) to give let7c/SNORD48. Similarly, to calculate the lowest signal to noise ratio, the yield for the least abundant Ago2 target (DICER1) was divided by the most abundant non-target RNA (GAPDH) to give DICER1/GAPDH. Values are rounded to 2 significant figures, and results with replicate RIPs are reported separately (RIP#1 & RIP#2).
The above experiment was repeated using an Ago1 antibody (clone 4B8, SAB4200084) instead of the Ago2 antibody. Although higher amounts of the 3 miRNAs were detected in Ago1 RIPs than in IgG RIPs or the non-target small RNAs in Ago1 RIP, yields were extremely low compared with Ago2 RIP (let7c = 0.4 to 1.7 %input with Ago1 compared with 20 to 90 %input with Ago2). Furthermore, the 2 target mRNAs (DICER1 and MYC) were not selectively recovered when compared with non-target mRNA (GAPDH; data not shown).
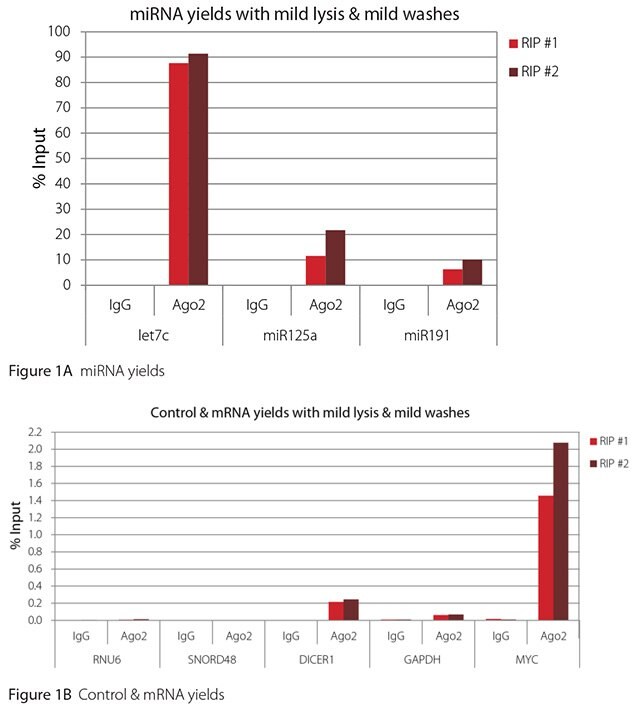
Figure 1. RT-qPCR results for Ago2 RIP with mild lysis and mild washes
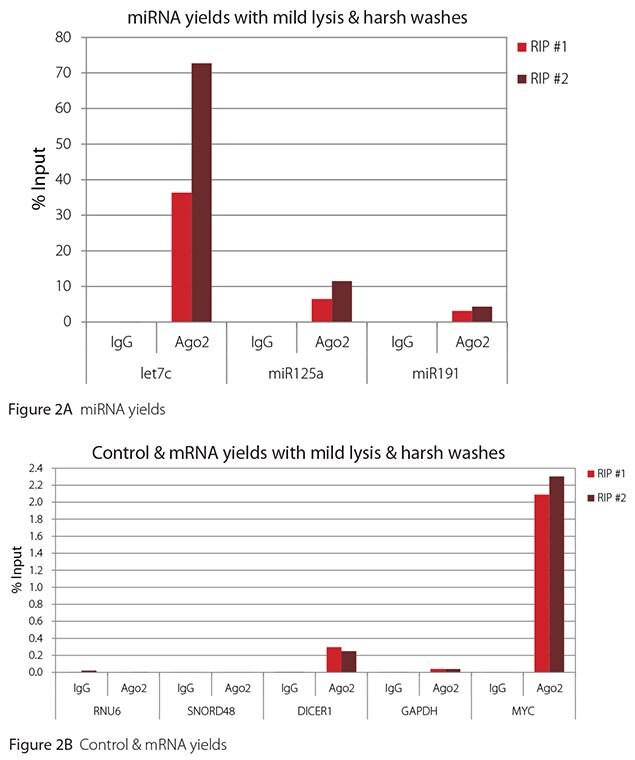
Figure 2. RT-qPCR results for Ago2 RIP with mild lysis and harsh washes
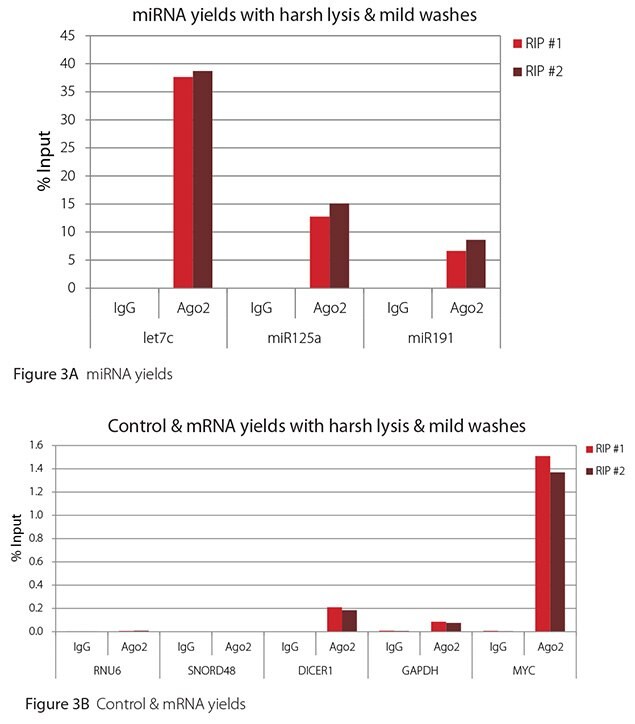
Figure 3. RT-qPCR results for Ago2 RIP with harsh lysis and mild washes
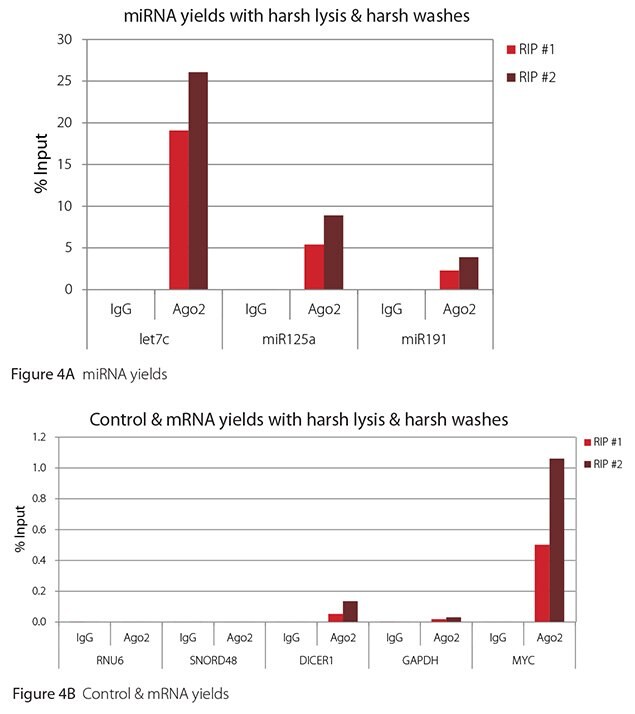
Figure 4. RT-qPCR results for Ago2 RIP with harsh lysis and harsh washes
Um weiterzulesen, melden Sie sich bitte an oder erstellen ein Konto.
Sie haben kein Konto?