76735
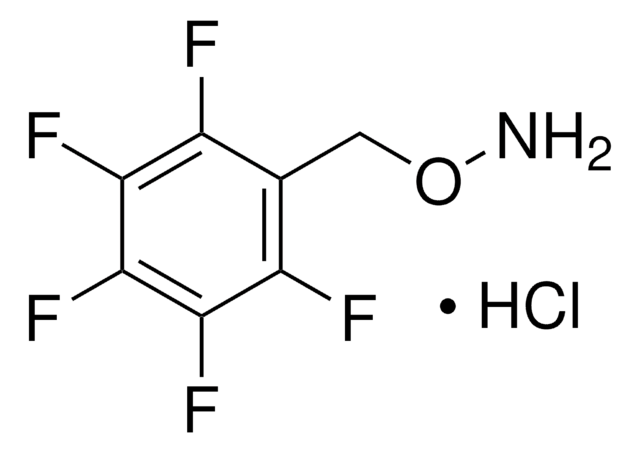
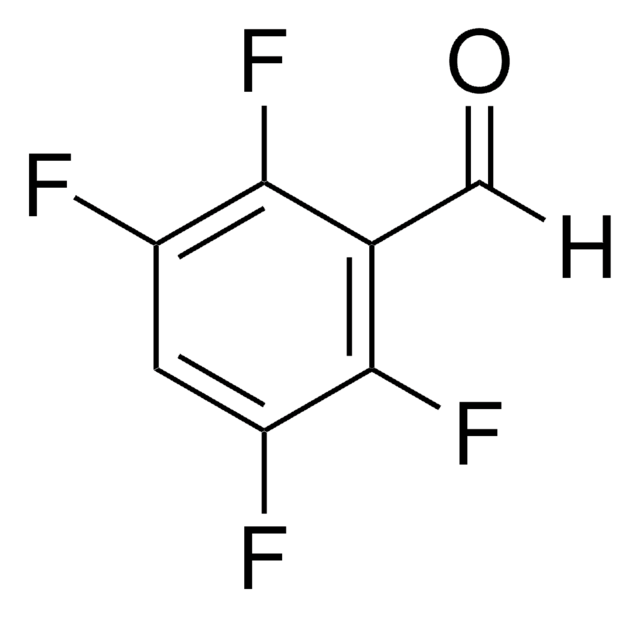
O-(2,3,4,5,6-Pentafluorobenzyl)hydroxylamine hydrochloride
for GC derivatization, LiChropur™, ≥99.0% (AT)
Synonym(s):
PFBHA·HCl
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
Select a Size
All Photos(2)
Select a Size
Change View
About This Item
Linear Formula:
C6F5CH2ONH2·HCl
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
249.57
Beilstein:
4031190
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12000000
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.22
Recommended Products
grade
for GC derivatization
Quality Level
Assay
≥99.0% (AT)
form
solid
quality
LiChropur™
reaction suitability
reagent type: derivatization reagent
reaction type: Alkylations
technique(s)
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
mp
212-218 °C
227 °C (subl.) (lit.)
solubility
H2O: 5%, clear
SMILES string
Cl.NOCc1c(F)c(F)c(F)c(F)c1F
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
O-(2,3,4,5,6-Pentafluorobenzyl)hydroxylamine hydrochloride (PFBHA.HCl) is a derivatizing agent.
Application
PFBHA.HCl has been used for derivatization of metabolites with carbonyl groups followed by analysis via GC-MS. It has also been used in aldehyde derivatization followed by aldehydic hydrolysis using GC/MS.
Packaging
Bottomless glass bottle. Contents are inside inserted fused cone.
Other Notes
Sensitive derivatizing agent for electron capture gas chromatographic analysis of carbonyl-containing compounds: keto steroids and carbohydrates
Legal Information
LiChropur is a trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Plasmalogen degradation by oxidative stress: production and disappearance of specific fatty aldehydes and fatty alpha-hydroxyaldehydes.
Stadelmann-Ingrand S
Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 31(10), 1263-1271 (2001)
Degradation of fluoranthene by Pasteurella sp. IFA and Mycobacterium sp. PYR-1:isolation and identification of metabolites.
Sepic E, Bricelj M, Leskovsek H.
Journal of Applied Microbiology, 85(4), 746-754 null
Birgit Schulze et al.
Analytical biochemistry, 348(2), 269-283 (2005-11-26)
A GC-MS-based method for the simultaneous quantification of common oxylipins along with labile and highly reactive compounds based on in situ derivatization with pentafluorobenzyl hydroxylamine to the corresponding O-2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzyl oximes (PFB oximes) is presented. The approach covers oxo derivatives such
Chunhui Deng et al.
Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences, 810(2), 269-275 (2004-09-24)
Analysis of breath acetone has been used as a diagnostic tool for diabetes. Due to its nature of volatility and activity, it is very difficult to accurately measure the concentration of acetone in human breath by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS).
Yun-Gon Kim et al.
Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences, 893-894, 177-181 (2012-03-31)
Nucleotide diphosphate (NDP) sugars are widely present in antibiotics and glycoconjugates, such as protein- and lipid-linked oligosaccharides, where they act as substrates for glycosyltransferase in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Among NDP sugars, NDP-4-keto sugars are key intermediates in the synthesis of
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service