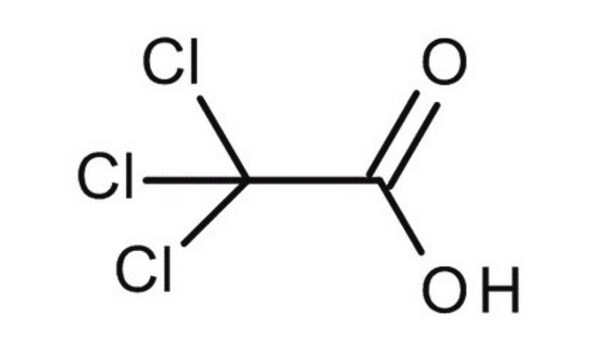
T0699
Trichloroacetic acid solution
6.1 N
Synonym(s):
TCA
About This Item
~100 % (w/v)
Recommended Products
form
liquid
Quality Level
concentration
6.1 N
~100 % (w/v)
SMILES string
OC(=O)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl
InChI
1S/C2HCl3O2/c3-2(4,5)1(6)7/h(H,6,7)
InChI key
YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- in indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) enzyme assay to hydrolyze N-formylkynurenine and produce kynurenine
- in the proliferation of human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (HPASMCs)
- to treat ground tissue and precipitate proteins during protein extraction and quantification
Biochem/physiol Actions
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Proteinase K (EC 3.4.21.64) activity can be measured spectrophotometrically using hemoglobin as the substrate. Proteinase K hydrolyzes hemoglobin denatured with urea, and liberates Folin-postive amino acids and peptides. One unit will hydrolyze hemoglobin to produce color equivalent to 1.0 μmol of tyrosine per minute at pH 7.5 at 37 °C (color by Folin & Ciocalteu's Phenol Reagent).
Proteinase K (EC 3.4.21.64) activity can be measured spectrophotometrically using hemoglobin as the substrate. Proteinase K hydrolyzes hemoglobin denatured with urea, and liberates Folin-postive amino acids and peptides. One unit will hydrolyze hemoglobin to produce color equivalent to 1.0 μmol of tyrosine per minute at pH 7.5 at 37 °C (color by Folin & Ciocalteu's Phenol Reagent).
Protocols
This procedure may be used for the determination of Amyloglucosidase activity using starch as the substrate.
To standardize a procedure for the determination of the enzymatic assay of choloylglycine hydrolase.
Proteinase K (EC 3.4.21.64) activity can be measured spectrophotometrically using hemoglobin as the substrate. Proteinase K hydrolyzes hemoglobin denatured with urea, and liberates Folin-postive amino acids and peptides. One unit will hydrolyze hemoglobin to produce color equivalent to 1.0 μmol of tyrosine per minute at pH 7.5 at 37 °C (color by Folin & Ciocalteu's Phenol Reagent).
This procedure may be used for all Ficin products.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service