WTA1
TransPlex® Whole Transcriptome Amplification Kit
DNA polymerase separate.
About This Item
Recommended Products
Related Categories
General description
Application
- qPCR
- microarray analysis
- cloning
Features and Benefits
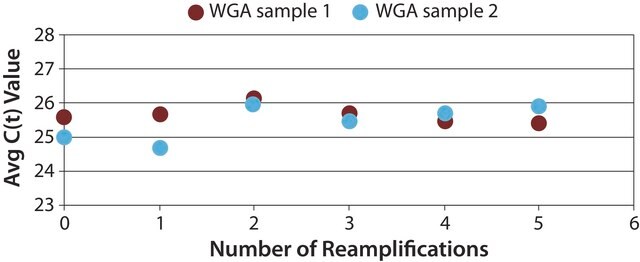
- Amplification of total RNA in less than 4 hours with less than 30 minutes of "hands-on" time
- Only 5 ng of starting material required to produce a highly representative library from total RNA
- Microgram quantities of amplification product generated from intact RNA from tissue, cultured cells, serum, or degraded RNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples
Principle
Legal Information
related product
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Epigenetic modifications are thought to occur through two key interconnected processes—DNA methylation and the covalent modification of histones.
Protocols
Amplification products generated by the TransPlex® WTA and Complete WTA2 kits are suitable for microarray target for expression analyses, and can be incorporated into existing Illumina workflows.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service