Peptide Modifications: N-Terminal, Internal, and C-Terminal
N-terminal, internal, and C-terminal peptide modifications are useful for a variety of applications, such as Western blotting, protein-protein interaction studies, and fluorescence-based assays. Use the table below for a list of various applications and to jump to more information, including structures and relevant references.
To request a quote on custom peptides or for help designing a custom PEPscreen® peptide library, follow the link below.
| Peptide Modification | Applications |
|---|---|
| Acetylation | Increase peptide stability by preventing N-terminal degradation |
| Biotin | Commonly used in immunoassays, histocytochemistry, and fluorescence based flow cytometry |
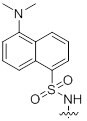
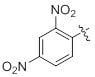
| Dansyl and 2, 4-Dinitrophenyl | Fluorescence based assays |
| Fluorescein and 7-methoxycoumarin acetic acid | Protein-protein interaction and localization studies |
| Palmitic Acid | Increase their cell permeability and help binding of the peptides to cell membrane |
| Cyclization (Disulfide bridge) | Stabilize the peptide conformation, increase bioactivity, and enzyme stability |
| Cysteine Carbamidomethylation (CAM) | Peptide Mass Fingerprinting for identification and characterization of peptides. To block cysteine residues from oxidation in protein assays |
| Phosphorylation | Gene expression, protein-protein interaction and signal transduction in plants and animals |
| Isotope labeled Amino Acids | Study protein interactions, proteins, post translation modifications such as ubiquitination and phosphorylation |
| Spacers | Reduce steric hindrance at the binding sites of the peptide and its load |
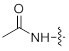
| Molecular Weight | 43 g/mol |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
References
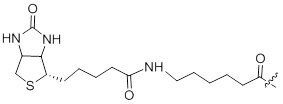
| Molecular Weight | 340 g/mol |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
References
| Molecular Weight | 249 g/mol |
| Excitation Wavelength | 372 nm |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
References
| olecular Weight | 167 g/mol |
| Excitation Wavelength | 354-400 nm |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
References

| Molecular Weight | 359 g/mol |
| Excitation/Emission Wavelength | 494/518 nm |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
References
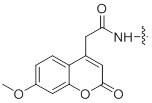
| Molecular Weight | 217 g/mol |
| Excitation/Emission Wavelength | 323/382 nm |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
References
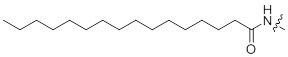
| Molecular Weight | 239 g/mol |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
References
| Molecular Weight | N/A |
| Availability: | PEPscreen®, AQUA™ Peptides |
References
2.2 Cysteine Carbamidomethylation (CAM)
Carbamidomethylation (CAM) is a deliberate post-translational modification introduced to cysteine residues by reacting with iodoacetamide. Peptides with this modification are mainly used in Peptide Mass Fingerprinting for identification and characterization of proteins1. In other assays, this process is used to block Cysteine from oxidation2.
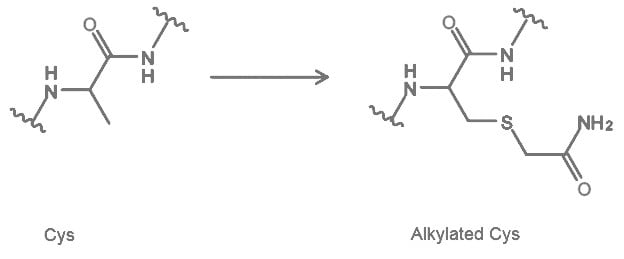
| Molecular Weight | 160 g/mol |
| Availability: | PEPscreen®, AQUA™ Peptides |
References
2.3 Isotope labeled Amino Acids
AQUA peptides are synthetic peptides with amino acids enriched in 18O, 13C, and/or 14N. They are similar to their native peptides in terms of chemical, physical properties and also their biological activities1. Main applications for these peptides are to study protein interactions, proteins, post translation modifications such as ubiquitination and phosphorylation2-5.
References
2.4 Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation can be performed on Tyr, Ser and Thr residues as a posttranslational modification (PTM) on peptides. Phosphorylated peptides have application in many cellular processes such as gene expression, protein-protein interaction and signal transduction in plants and animals1,2.

| Molecular Weight | 82 g/mol |
| Availability: | PEPscreen®, AQUA™ Peptides |
References
2.5 Spacers
Spacers are used to create a distance between the peptide and the cargo to reduce steric hindrance at the binding sites of the peptide. In this case cargo can be a drug, dye, tag.
2.5.1 PEGylation
Attachment of poly (ethylene glycol) to a peptide is called PEGylation. Short bifunctional PEG (Poly (ethylene glycol)) can be used as a spacer in bioconjugation of peptides with other molecules. PEG bioconjugation has also been used to improve proteolytic stability, biodistribution and solubility of peptides1-2.
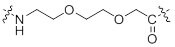
| Molecular Weight | 146 g/mol |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
References
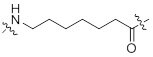
| Molecular Weight | 113 g/mol |
| Availability: | PEPscreen® |
Reference
3.0 C-Terminal Modifications
3.1 Amide (Amidation)
The C-terminal of the peptide is synthesized as an amide to neutralize negative charge created by the C-terminal COOH. This modification is added to prevent enzyme degradation, to mimic native proteins, and in some cases to remove hydrogen bonding at the C-terminal of the peptides which may interfere with the assays.1
Reference
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?