C1389
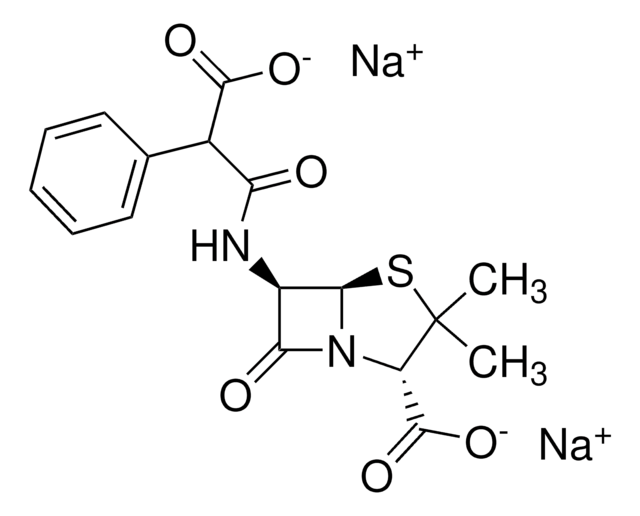
Carbenicillin disodium salt
89.0-100.5% anhydrous basis
Synonym(s):
Carbenicillin, Disodium carbenicillin, α-Carboxybenzylpenicillin disodium salt
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic (chemical)
Quality Level
Assay
89.0-100.5% anhydrous basis
form
powder
color
white to off-white
solubility
H2O: 50 mg/mL
antibiotic activity spectrum
Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
Mode of action
cell wall synthesis | interferes
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
[Na+].[Na+].CC1(C)S[C@@H]2[C@H](NC(=O)C(C([O-])=O)c3ccccc3)C(=O)N2[C@H]1C([O-])=O
InChI
1S/C17H18N2O6S.2Na/c1-17(2)11(16(24)25)19-13(21)10(14(19)26-17)18-12(20)9(15(22)23)8-6-4-3-5-7-8;;/h3-7,9-11,14H,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23)(H,24,25);;/q;2*+1/p-2/t9?,10-,11+,14-;;/m1../s1
InChI key
RTYJTGSCYUUYAL-YCAHSCEMSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Carbenicillin is commonly used in cell biology applications to prevent the growth of bacterial contaminants. It is also used in microbiology to select for bacteria that have been transformed with a vector harboring the gene encoding beta-lactamase, which makes them resistant to carbenicillin.
Application
- in the preparation of Luria-Bertani (LB) agar plates and media
- as a selective agent in the culture media to prevent the growth of bacterial contaminants
- in a study focused on the development of monoclonal antibodies
Biochem/physiol Actions
Antimicrobial spectrum: Active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
Features and Benefits
- Broad-spectrum antibiotic with bactericidal and beta-lactamase resistant activity
- Effective against a wide range of bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Commonly used in Cell Biology and Biochemical applications
- Offers greater stablility than ampicillin
Storage and Stability
Analysis Note
Other Notes
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service